Figure 1.
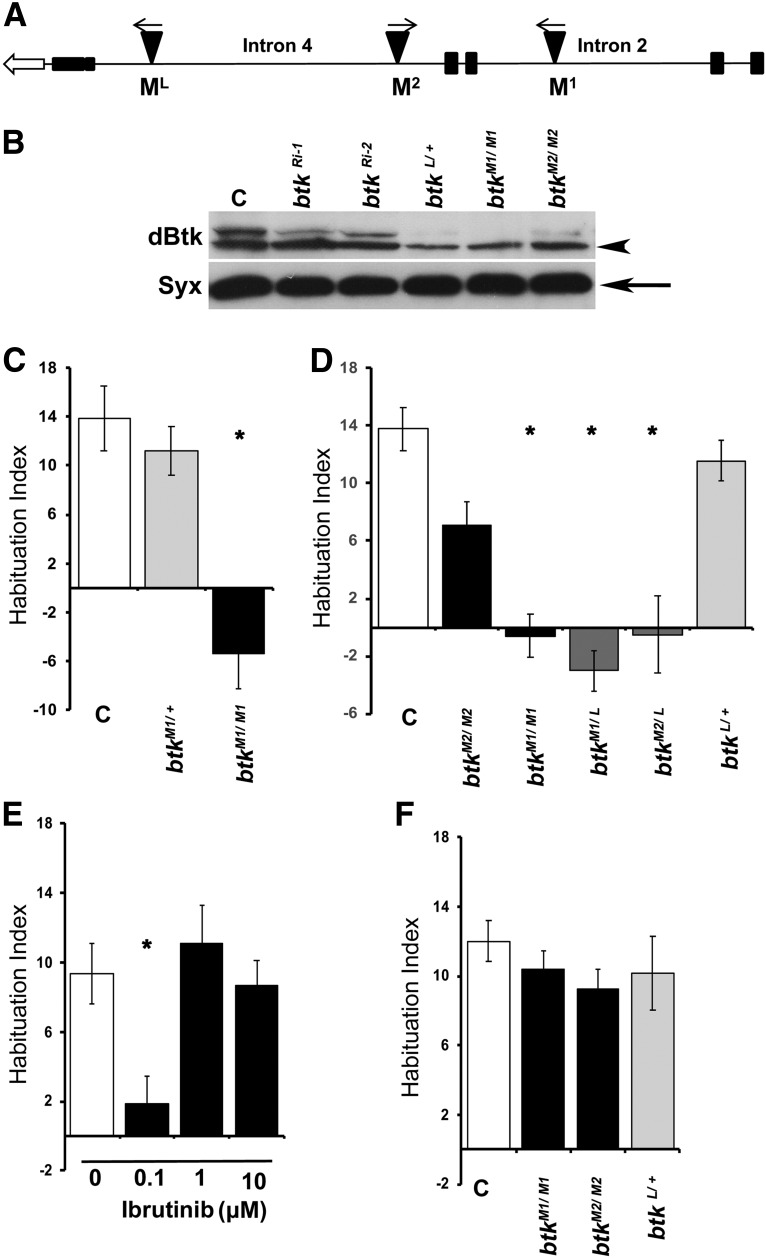
dBtk is essential for footshock habituation. A, A schematic of the Btk29A (dBtk) genomic area where the transposon insertions used in this study reside. The open arrow demonstrates the direction of transcription. Filled boxes correspond to exons, whereas lines correspond to the indicated introns. The triangles show the MiMIC insertions. M1, The homozygous viable MI01270; M2, the homozygous viable MI02160; ML, the lethal insertion MI02966. B, Western blot analysis of head lysates from five 3- to 5-d-old female btk mutants and pan-neuronally expressing RNAis as indicated. The arrowhead points to a band which migrates as predicted for the long (type 2) dBtk protein, whereas the arrow points to the apparent short (type 1) isoform (Hamada-Kawaguchi et al., 2014). The following strains were used: C, Control (y1w*); btkRi-1, pan-neuronal expression under Elav-Gal4 of the BDSC 35159 RNAi-encoding transgene; btkRi-2, pan-neuronal expression under Elav-Gal4 of the BDSC 25791 RNAi-encoding transgene; btk L/+, heterozygotes for the lethal (MI02966) insertion; btk M1/M1, homozygotes for the M1 (MI01270) insertion; btk M2/M2, homozygotes for the M2 MI02160) insertion. The anti-dBtk antibody (Btk) recognizes two bands, the upper one of which is reduced the most in all mutants and RNAi-expressing animals, with the lower one also reduced, albeit to a lesser degree. Syntaxin 1 (Syx) is used as a loading control. C–F, Habituation indices quantify the difference in footshock avoidance following exposure to 15 stimuli from that of same genotype naive flies and are shown as the mean ± SEM for the indicated number of repetitions (n). Stars indicate significant differences from controls as indicated in the text. C, Homozygous btkM1/M1 mutants perform significantly different from mutant heterozygotes and y1w* controls (C). n ≥ 16 for all groups. D, Complementation of the habituation failure among dBtk insertion mutants. Although the performance of btkL heterozygotes was not significantly different from that of the y1w*controls (C), hetero-allelics of this lethal insertion over both viable M1 and M2 insertions presented significant habituation deficits. n ≥ 9 for all groups. E, The Btk inhibitor Ibrutinib induces habituation deficits in y1w* control flies in a dose-specific manner. 0 represents y1w*animals fed the DMSO vehicle and compared with their performance; 0.1μm Ibrutinib induced a significant deficit, but higher doses did not. n ≥ 9 for all groups. F, dBtk mutants do not present habituation deficits to 4 min exposure of the aversive odorant OCT. n ≥ 12 for all groups.