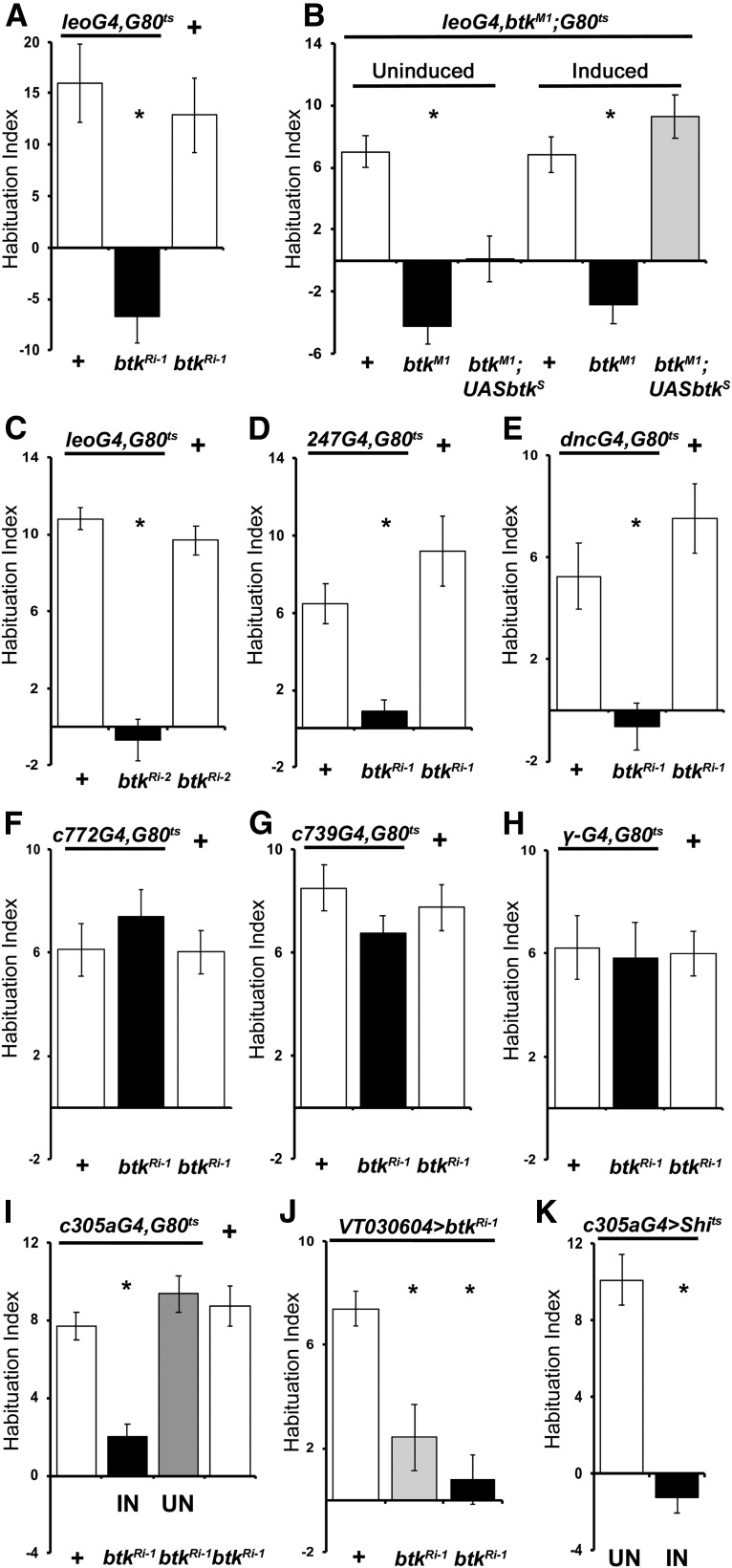
Figure 3.
dBtk is acutely required within the α′/β′ mushroom body neurons to facilitate habituation to footshock. Habituation indices quantifying the difference in footshock avoidance following exposure to 15 stimuli from that of same genotype naive flies are shown as the mean ± SEM for the indicated number of repetitions (n). All panels show the performance of animals expressing a dbtk RNAi-encoding transgene (btkRi-1/+) under the indicated driver (black bar), the driver heterozygotes (left open bars), and the RNAi-mediating transgene heterozygotes (+, right open bars). driver/+, Progeny from the cross of the w1118 background driver with 36303 y1v1, whereas for the btkRi-1/+, the y1v1 background btkRi-1 was crossed to w1118 so that the two controls have equivalent backgrounds as the experimental. Asterisks indicate significant differences from controls as detailed in the text. A, Adult limited pan-MB expression of btkRi-1 eliminates habituation to 15 footshocks. n ≥ 11 for all groups. B, Rescue of the habituation deficit of btkM1/M1 by adult-limited expression of a dBtk transgene in the MBs. Uninduced (left side) transgene-bearing flies (gray bar) behave significantly different from controls, much like non-transgene bearing mutants homozygotes (p = 0.0014 and p = 2.2 × 10−6, respectively). In contrast, a 2 d induction of the transgene (gray bar right side) completely reversed the deficient habituation (p = 0.1918 vs p = 6 × 10−6 for mutant homozygotes compare to controls; open bar). n ≥ 8 for all groups. C, Adult limited pan-MB expression of the independent btkRi-2 transgene precipitates defective shock habituation compared with both controls. n ≥ 10 for all groups. D, Adult specific expression of btkRi-1 under the independent pan-MB 247Gal4 driver results in abrogated shock habituation compared with controls. n ≥ 14 for all groups. E, A third MB-restricted driver (dncGal4) yields adult-specific shock habituation deficits when driving UAS-btkRi-1. n ≥ 9 for all groups. F, Adult-limited btkRi-1 expression in α/β MB neurons does not precipitate habituation deficits. n ≥ 11 for all groups. G, Adult-specific btkRi-1 expression in α/β MB neurons under the independent c739Gal4 driver does not compromise shock habituation. n ≥ 13 for all groups. H, Adult-specific btkRi-1 expression in γ MB neurons under VT030604 also does not compromise shock habituation. n≥14 for all groups. I, Adult-specific IN of btkRi-1 expression in α′/β′ MB neurons abrogates shock habituation, whereas the uninduced transgene (UN) does not. n ≥ 9 for all groups. J, Expression of btkRi-1 driven by theα′/β′-specific VT030604 driver present aberrant habituation (black bar) when induced for 2 d compared to their uninduced siblings. However, when flies were raised at 25°C (gray bar), they presented an ameliorated deficit compared with those raised at 18°C and uninduced. n ≥ 14 for all groups. K, Expression of shits in α′/β′ MB neurons compromises habituation under the restrictive conditions (black bar) compared with animals kept under permissive temperature (p = 9 × 10−8). n ≥ 11 for all groups.