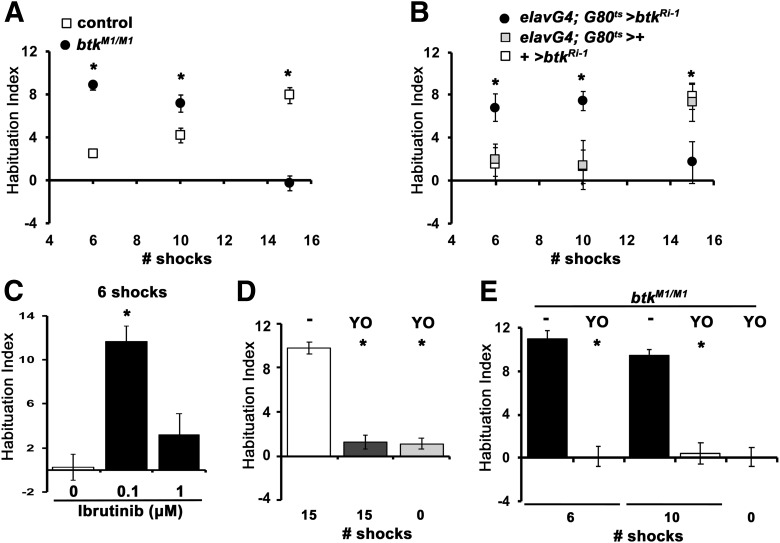
Figure 4.
dBtk is acutely required within α/β MB neurons to inhibit premature habituation to footshock. Habituation indices quantifying the difference in footshock avoidance following exposure to the indicated number of stimuli from that of same genotype naive flies are shown as the mean ± SEM for the indicated number of repetitions (n). Filled circles represent the mean performance of animals with abrogated dBtk, whole open squares the respective controls. Stars indicate significant differences from controls as detailed in the text. A, Footshock habituation of controls (y1w*) and btkM1/M1 mutants after prior experience of 6, 10, and 15 shocks. The performance of controls is significantly different from that of the mutants after 6, 10, and 15 footshocks. n > 13 for all groups. B, Adult-limited pan-neuronal expression of btkRi-1 recapitulates both the premature habituation after 6 and 10 shocks and the habituation failure after 15 stimuli. So that the controls have similar genetic backgrounds, progeny from the cross of the w1118 background ElavGal4;Gal80ts with 36303 y1v1, whereas for the btkRi-1 /+, the y1v1 background btkRi-1 was crossed to w1118. n≥11 for all groups. C, Ibrutinib promotes premature habituation after 6 shocks at 0.1 μm, but not at 1 μm relative to the performance of vehicle-treated y1w* animals. n ≥ 8 for all groups. D, Dishabituation in y1w* flies after 8 s of YO puff. White bar, Habituation after 15 shocks; dark gray bar, dishabituation with YO after experiencing 15 shocks; light gray bar, the effect on avoidance of YO on naive flies before testing their shock avoidance. YO exposure has significant effects on reversing the habituated response, but YO exposure of naive flies does not affect their shock avoidance (0). n ≥ 10 for all groups. E, The reduced avoidance of btkM1/M1 mutants after 6 and 10 footshocks is bona fide premature habituation because it is reversible (dishabituated) by a single puff of YO after the respective footshocks as indicated. Black bars denote habituation without YO and the open bars after odor presentation. 0 denotes shock avoidance of naive flies after YO exposure. YO exposure results in significant dishabituation after 6 and 10 shocks. n ≥ 8 for all groups.