Figure 2.
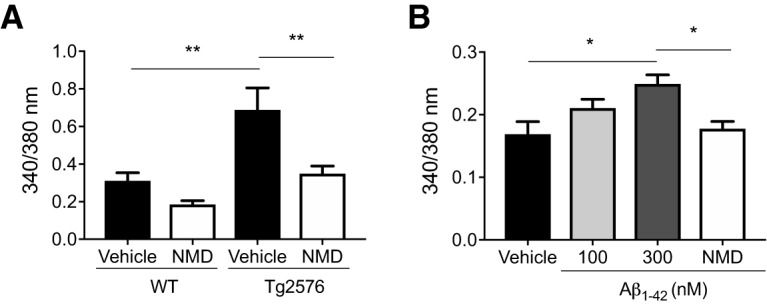
Arcuate NPY neurons from Tg2576 brain slices or exogenous Aβ1–42-treated WT brain slices have increased cytoplasmic-free Ca2+ levels that can be reversed by the L-type Ca2+ channel blocker nimodipine (NMD). A, Arcuate NPY neurons from Tg2576 mice have increased cytoplasmic-free Ca2+ levels compared with WT mice that are decreased by nimodipine. Cytoplasmic-free Ca2+ was measured using fura-2 AM in arcuate NPY neurons isolated by enzymatic digestion from WT or Tg2576 mice. After obtaining baseline levels, cells were perfused with nimodipine (2 μm). n = 18–21 cells from ≥ 3 mice per group. Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA (F(3,74) = 9.738, p < 0.0001, followed by post hoc Tukey's multiple comparisons). **p < 0.01. B, Exogenous Aβ1–42-treated arcuate NPY neurons from WT mice have increased cytoplasmic-free Ca2+ levels that are decreased by nimodipine. Cytoplasmic-free Ca2+ was measured using fura-2 AM in arcuate NPY neurons isolated by enzymatic digestion from WT mice. After obtaining baseline levels, cells were first perfused with oligomeric Aβ1–42 (100 or 300 nm) followed by nimodipine (2 μm). n = 4 or 5 cells from 2 mice per group. Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA (F(3,14) = 5.028, p = 0.0143, followed by post hoc Tukey's multiple comparisons). *p < 0.05. Data are mean ± SEM.
