Figure 1.
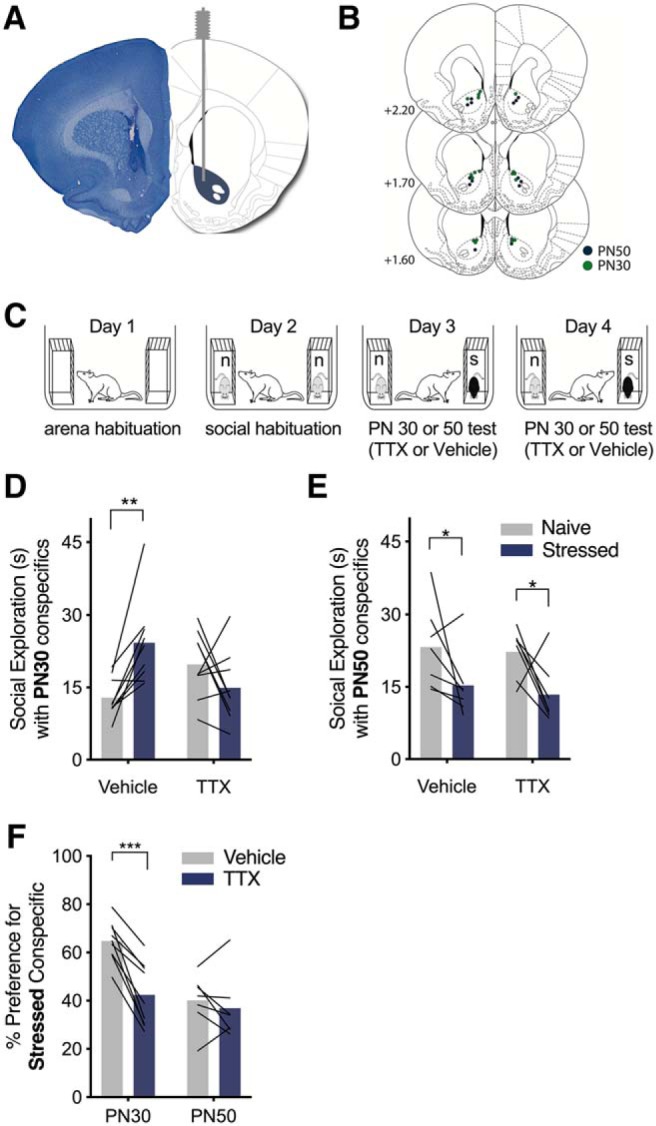
Pharmacological inhibition of the NAc abolished the social affective preference for stressed PN30, but not PN50, conspecifics. A, Representative image of a cannula tract in NAc (left) and corresponding rat brain atlas diagram (right). B, Map of bilateral cannula tip placements in NAc from experimental rats tested with PN30 (green; n = 9) and PN50 (blue; n = 7) conspecifics. C, Diagram of SAP test procedure with naive (n) and stressed (s) conspecifics. D, Mean (with individual replicates) time spent exploring the naive and stressed PN30 conspecifics during the 5 min trial. Vehicle-treated rats preferred to explore stressed PN30 conspecifics compared with naive PN30 conspecifics (p = 0.006), which was abolished via bilateral infusion ofTTX (100 nm, 0.5 μl/side) in NAc 15 min before testing (p = 0.203). E, Mean (with individual replicates) time spent exploring the naive and stressed PN50 conspecifics during the 5 min trial. Both vehicle-treated (p = 0.031) and TTX-treated (p = 0.020) rats preferred to explore naive PN50 conspecifics compared with the stressed PN50 conspecifics. F, Mean (with individual replicates) data from D and E shown as the percentage of total social exploration time that was spent investigating the stressed conspecific. Rats tested with PN30 conspecifics show preference (as indicated by scores >50%) for the stressed conspecific under vehicle treatment, which was significantly reduced after pharmacological inactivation of NAc with TTX (p = 0.0001). Rats tested with PN50 conspecifics show a preference for naive conspecifics, which was unaffected by TTX treatment (p = 0.452). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
