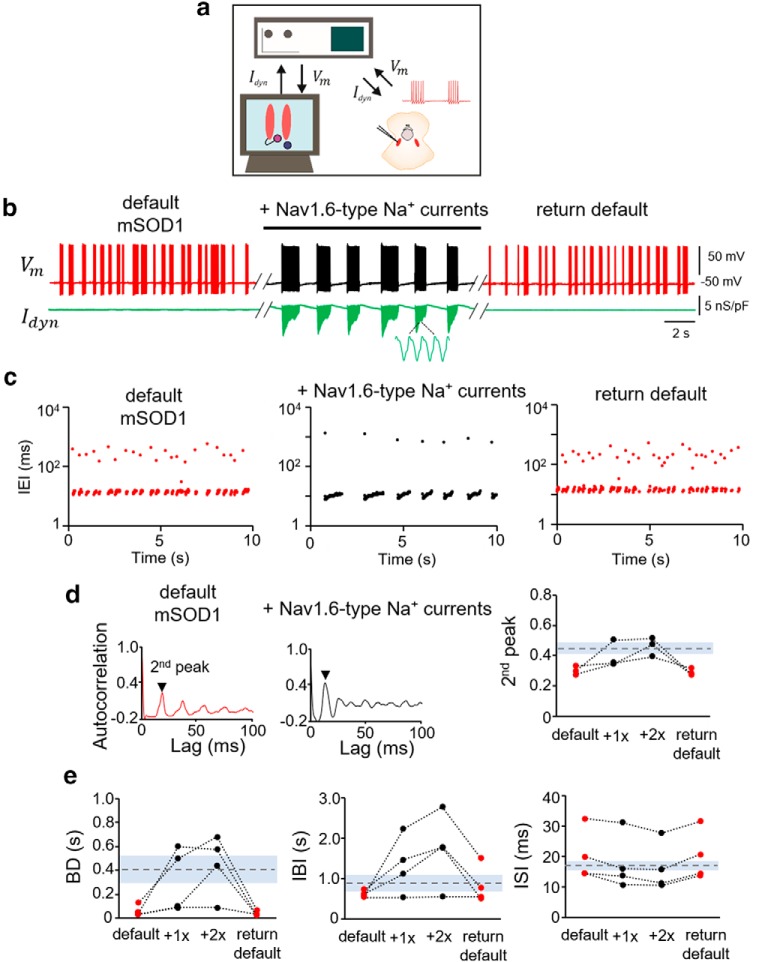
Figure 5.
Rescue of Nav 1.6-type sodium currents in mSOD1 Mes V neurons using dynamic clamp. a, Schematic shows the dynamic-clamp setup used to introduce conductance-based models of Nav1.6-type Na+ currents into mSOD1 Mes V neurons in real time during whole-cell patch-clamp recording. Idyn is the computer-generated model Na+ current in combination with a step depolarization to drive the patched Mes V neuron. Vm is the measured membrane voltage. b, Representative traces showing the membrane voltage in a bursting mSOD1 Mes V neuron with control/default behavior (left, red), followed by addition of Nav1.6-type currents (middle, black), which restores WT-like rhythmic bursting; subsequent removal of added currents returns default mSOD1 behavior (right red) in this neuron. Bottom, Green trace represents Idyn. c, Time series plots of IEIs (log scale) for the three different conditions in b. Each dot represents an interval between two consecutive spikes. d, Autocorrelation function of the membrane voltage for default mSOD1 (left) and with addition of Nav1.6 currents (middle). The height of the second autocorrelation peak highlights rhythmicity (arrowhead). Right, Measured second peak values for 4 mSOD1 cells. Dashed horizontal line indicates average WT values. Gray shaded region represents ±SD. e, Treatment effects on burst characteristics, including burst duration (BD), IBIs, and ISIs within bursts (ISI) shown for various mSOD1 cells tested under the different conditions as in b. Dashed lines indicate average WT values. Gray regions represent ± SD.