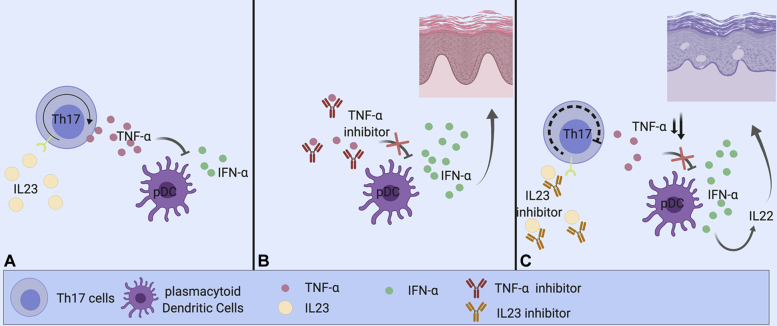
Fig 2.
Effect of IL-23 inhibition on TNF-α and IFN-α. (Created with BioRender.com.) A, IL-23 induces upregulation of TNF-α through TH17 cells. TNF-α inhibits plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC) secretion of IFN-α, a known inducer of inflammatory skin lesions. B, Inhibition of TNF-α by a TNF-α inhibitor can lead to an unopposed increase in IFN-α, resulting in inflammatory skin lesions. C, As IL-23 induces upregulation of TNF-α through TH17 cells, one could argue that an IL-23 inhibitor partially acts as a TNF-α inhibitor. Through this mechanism, it could increase IFN-α, possibly explaining the paradoxical skin reaction in our patient.