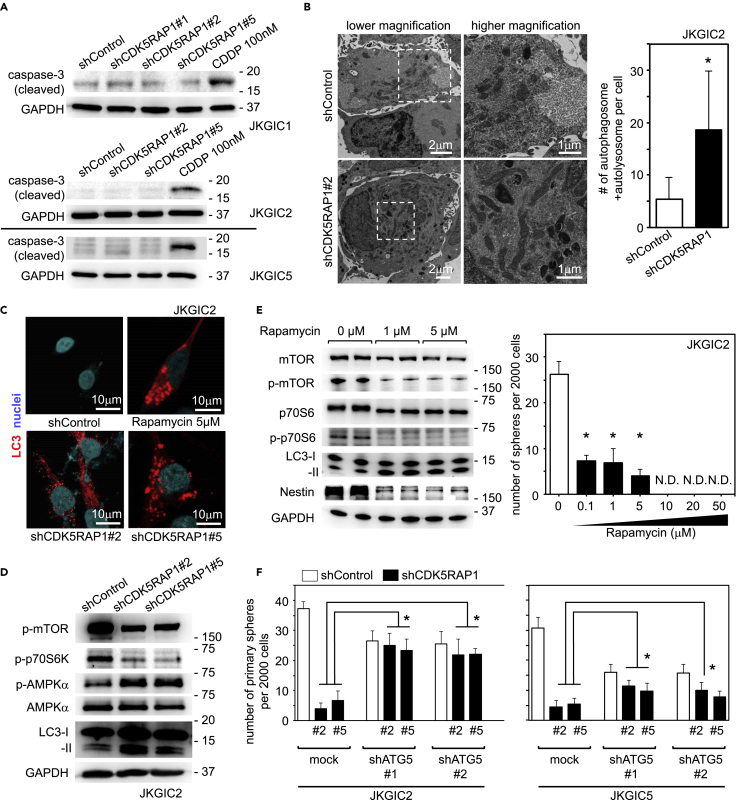
Figure 3.
CDK5RAP1 Knockdown Induces Excessive Autophagy, Which Critically Determines GIC Fate
(A) CDK5RAP1 knockdown did not activate caspase-3 in JKGIC1, JKGIC2, and JKGIC5 cells. CDDP-treated cells served as a positive control of apoptotic status.
(B) Left: Representative electron microscopy images of the autophagic response. JKGIC2 cells were fixed after 4 days of lentiviral transduction of each shRNAs. Right: CDK5RAP1 knockdown increased the number of autophagosomes and autolysosomes. n = 5 per condition. *p = 0.0391 versus shControl. Scale bars, 1 μm.
(C) Representative immunostaining images for LC3 in JKGIC2 cells. CDK5RAP1 knockdown induces LC3 puncta formation. Rapamycin-treated cells served as a positive control of LC3 puncta formation. Scale bars, 10 μm.
(D) Immunoblotting analyses of mTOR, AMPK, and LC3 show that CDK5RAP1 knockdown activates the autophagic program in JKGIC2 cells.
(E) Left: mTOR inhibition with rapamycin triggers the autophagic response and decreases Nestin expression in JKGIC2 cells. n = 5 per condition. Right: Dose-dependent effect of rapamycin on the number of spheres formed from 2,000 JKGIC2 cells. Each bar represents the SD value from four independent replicates. *p < 0.05.
(F) Comparison of sphere formation by JKGIC2 and JKGIC5 cells transfected with shRNAs against CDK5RAP1 in the presence or absence of shRNAs against ATG5. ATG5 knockdown reduces the sphere-forming capacity but successfully rescues the shCDK5RAP1-mediated decrease in the anchorage-independent growth of GICs. Each bar represents the SD value from four independent replicates. *p < 0.05.
Also see Figure S3.