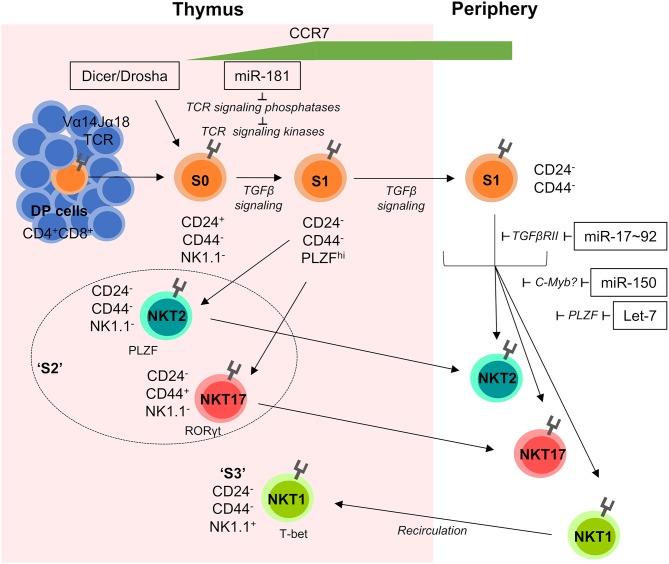
Figure 1.
miRNA-mediated control of iNKT-cell development. iNKT cells are selected on CD1d-expressing DP cells in the thymus. Subsequently they progress through distinct developmental stages S0–S3 characterized by their dynamic expression of CD24, CD44, NK1.1, and the transcription factors PLZF, RORγt, and T-bet. Early stage iNKT cells are sensitive to the loss of total miRNAs in Dicer and/or Drosha-deficient mice and require fine-tuned TGFβ and TCR signaling for normal development. S1 cells begin to upregulate the chemokine receptor CCR7, which promotes migration to the medulla and is detectable on the surface of recent thymic emigrants (RTEs). S2 cells exit the thymus and travel to peripheral tissues, whilst S3 cells recirculate back into the thymus and remain resident for extended periods of time. Individual miRNAs acting on distinct developmental transitions and their targets are indicated. Double positive (DP), Stage 0 (S0), Stage 1 (S1), Stage 2 (S2), and Stage 3 (S3).