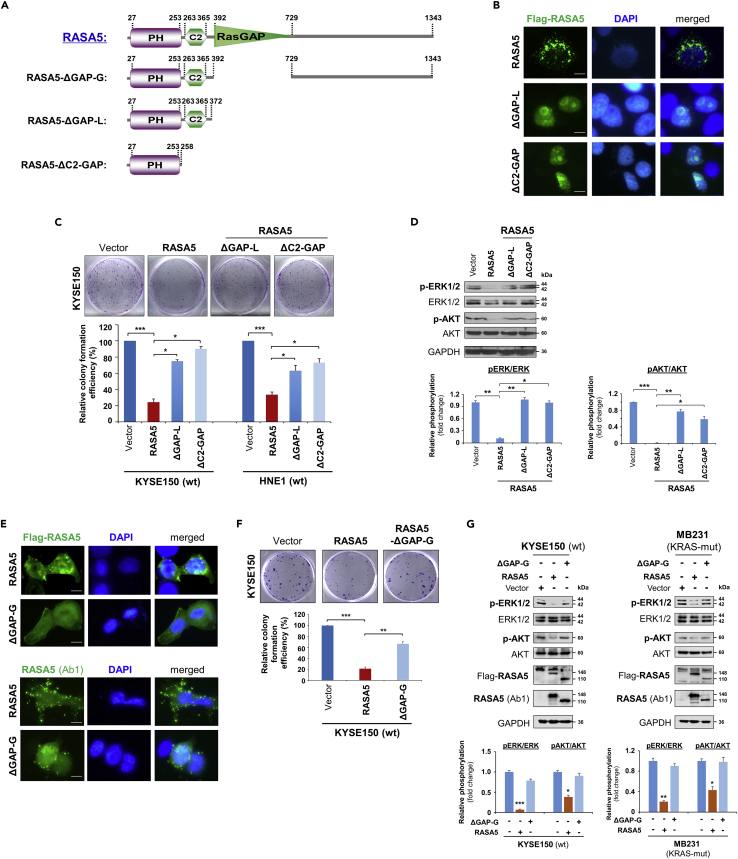
Figure 7.
RASA5 Exerts Its Tumor Suppressive Function Dependent on its GAP Domain
(A) Schematic view of full-length RASA5 (wild type) and three truncated mutants (RASA5ΔGAP−G, RASA5ΔGAP−L, RASA5ΔC2−GAP). ΔGAP-G: RASA5 with only RasGAP domain deleted; ΔGAP-L: RASA5 with PH and C2 domains remained; ΔC2-GAP: RASA5 with C2 and RasGAP domains deleted.
(B and E) Representative immunofluorescence analysis of subcellular localization of wild-type RASA5 and truncated mutants, RASA5ΔGAP−L and RASA5ΔC2−GAP mutants (B); RASA5ΔGAP−G mutant (E), labeled with anti-Flag antibody (green) or anti-RASA5 (Ab1, ThermoFisher). Nuclei marked by DAPI (blue). Original magnification, 400x. Scale bar 200 μM.
(C and F) Effects of deletions of GAP domain and C2-GAP tandem on cell growth by colony formation assay. KYSE150 cells transiently transfected with plasmid expressing RASA5 or either of the three mutants, RASA5ΔGAP−L and RASA5ΔC2−GAP mutants (C); RASA5ΔGAP−G mutant (F). Number of colonies was presented in a bar graph (data were mean ± SEM of three independent experiments, *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001). Data were presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments by One Way ANOVA with multiple comparison post hoc analysis and representative data were shown.
(D and G) Western blot of phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and AKT in tumor cells with expression of RASA5 or three truncated mutants. (D) Effects of RASA5 and two indicated RASA5 mutants on ERK1/2 and AKT phosphorylation in KYSE150 cells. (G) Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and AKT in KYSE150 and MB231 cells with expression of RASA5 and RASA5ΔGAP−G mutant. Graphs represent quantification of the phosphor-immunoblots normalized to corresponding total protein levels (lower panel). Data were presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments by One Way ANOVA with multiple comparison post hoc analysis and representative data were shown. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.