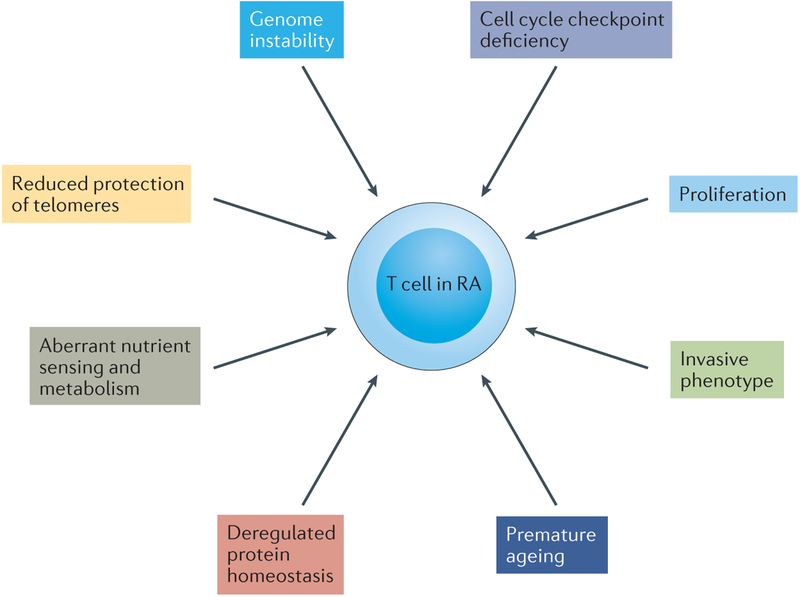
Figure 2. Emerging hallmarks of T cells in rheumatoid arthritis.
Core hallmarks of T cells in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are their ability to massively proliferate and to differentiate into proinflammatory effector cells. Several changes in the basic biologic pathways listed here distinguish T cells in healthy individuals from those in patients with RA and enable such T cells to deviate from their protective role to an autoinflammatory one. The molecular defects underlying pathogenic T-cell behaviour are currently being discovered; among them is the reprogramming of cellular metabolism, which fuels the functional capabilities of arthritogenic T cells.