Fig. 5. Effects of hypochlorite on 4F and apoA-I mediated cholesterol efflux.
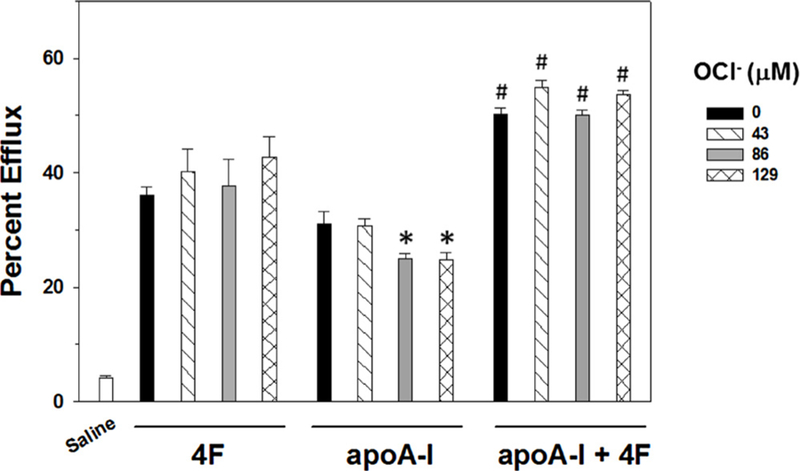
ABCA1-dependent cholesterol efflux to 4F (100 μg/mL) or apoA-I (100 μg/mL) was measured in the presence of increasing concentrations of hypochlorite (OCl−). Hypochlorite did not influence 4F-dependent efflux. In contrast, apoA-I mediated efflux was inhibited by 86 and 129μM hypochlorite. Mixing 4F and apoA-I resulted in a greater increase in cholesterol efflux than that seen with either treatment alone. Further, 4F abolished the inhibitory effect of hypochlorite on apoA-I -mediated cholesterol efflux. Data are the mean ± SEM (N = 6–12 per treatment group). * denotes a significant difference (P < 0.05) compared to apoA-I treatment with 0 or 43μM hypochlorite. # denotes a significant difference (P < 0.05) compared to the corresponding hypochlorite treatment of 4F or apoA-I alone.
