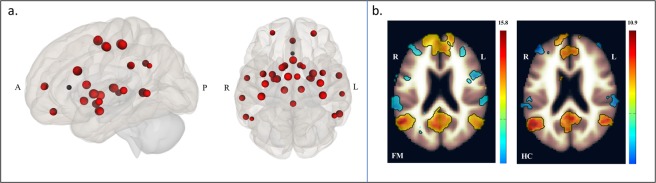
Figure 2.
Pain matrix rs-fMRI seed-based correlation analysis. (a) 3D image of the pain matrix: ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; PCC, posterior cingulate cortex; BA41, primary auditory cortex; AMYG, amygdala; AnG, angular gyrus; CAU, caudate; GP, globus pallidus; PUT, putamen; INS, insular cortex; mPFC, medial prefrontal cortex; PAG, periaqueductal gray matter; M1, primary motor cortex; SI, primary somatosensory cortex; SII, secondary somatosensory cortex; SMA, supplementary motor area; STS, superior temporal sulcus; THA, thalamus. (b) Connectivity maps of the pain matrix for FM (left) and HC (right) respectively. We calculated the BOLD mean time-series of all 34 seeds into one single a priori brain mask, and correlated it with the rest of the whole brain. Colors show either positive (red–yellow) or negative (blue–light blue) correlations of the pain matrix. Image shows positive correlations of the pain matrix with the Default Mode Network (DMN), with areas such as mPFC, PCC, PCN, and AnG.