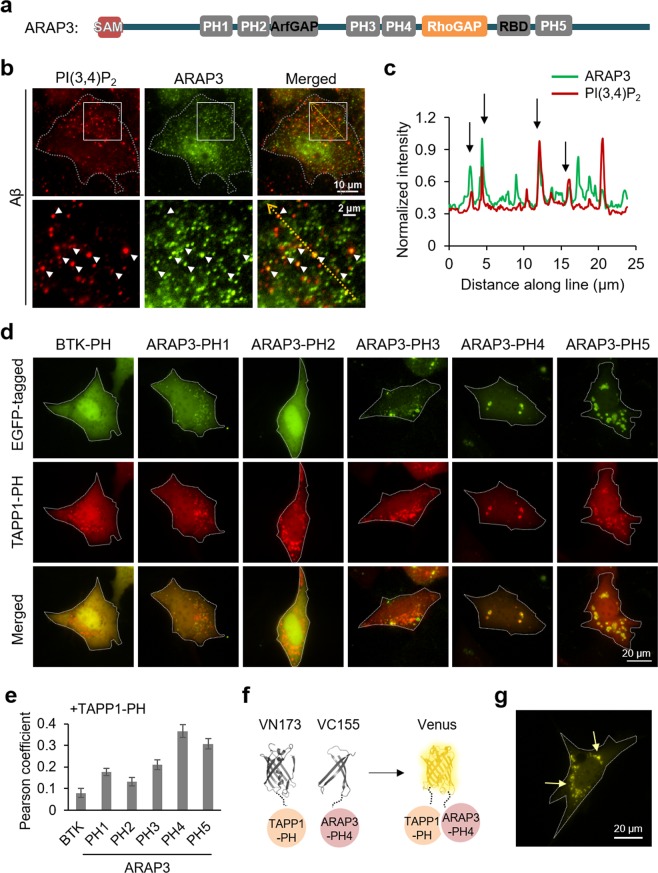
Figure 2.
ARAP3 can be associated with PI(3,4)P2-containing vesicles via its PH4 domain. (a) The scheme of ARAP3 domains. (b) ARAP3 (green) is partially localized at PI(3,4)P2-containing vesicles (red) in HT22 cells treated with 1 μM of Aβ for 24 hr. Lower panels show the boxed areas of upper panels at high magnification. (c) Intensity profiles of PI(3,4)P2 and ARAP3 across the yellow line in the merged image shown in (b). (d) EGFP-tagged each PH domain of ARAP3 (green), mKate2-TAPP1 (red) and merged images of HT22 cells after 48 hr starvation. Btk PH domain-EGFP was used as control. (e) Pearson coefficient was calculated to measure colocalization between TAPP1-PH and each ARAP3-PH construct (n = 16, 61, 64, 34, 49, 30 for Btk PH, ARAP3 PH1, PH2, PH3, PH4 and PH5, respectively) (f,g) BiFC design of VN173-TAPP1 PH domain and VC-155-ARAP3 PH4 domain (f) and BiFC signal in HT22 cells after 48 hr starvation (g). Yellow arrows highlight the BiFC signal at vesicles.