Figure 4.
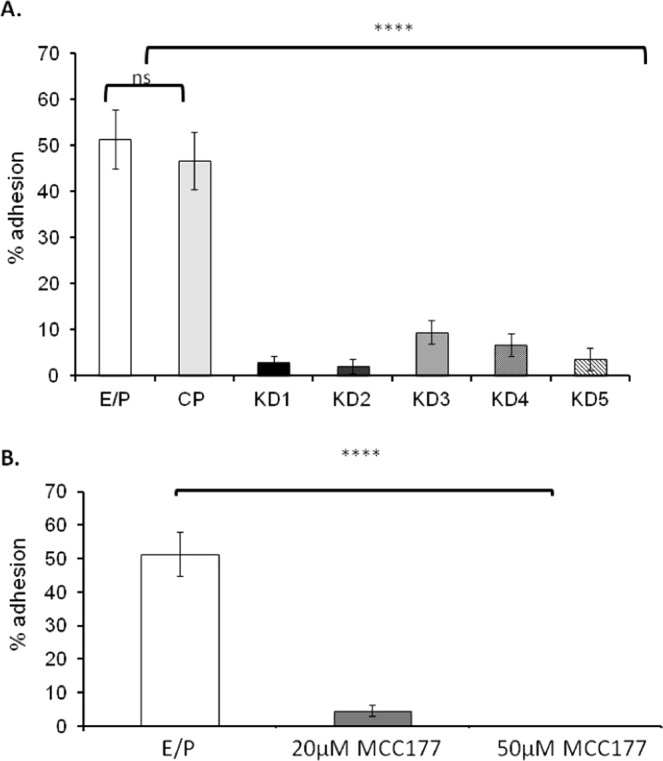
Knock down transfection of SOX17 in ECC-1 cells and inhibition using a chemical inhibitor results in decreased adhesion of ‘blastocyst-mimic’ spheroids. Knockdown transfection of ECC-1 cells with a CRISPR/Cas9 SOX17 knock-down plasmid mediated a significant reduction in spheroid adhesion across all knock-down cell clones (A, KD1-5) when compared to untransfected control ECC-1 cells (A, E/P) and ECC-1 cells transfected with a control plasmid (A, CP,****p < 0.0001). Inhibition of the group F Sox proteins using 20 μM MCC177 (B, Sox F inhibitor) resulted in a significant decrease in spheroid adhesion (****p < 0.0001), while 50 μM MCC177 completely inhibited spheroid adhesion (****p < 0.0001). Data presented as mean ± SEM, n = 5.
