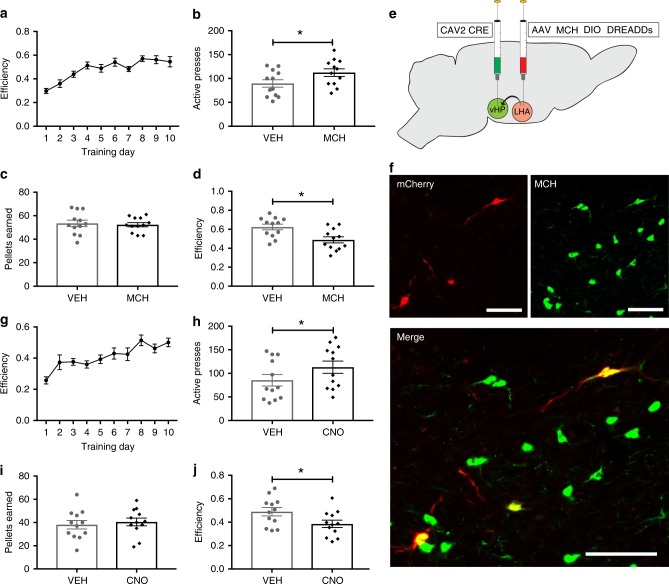
Fig. 3.
Activation of MCH-vHP signaling increases food impulsivity. a–d Effects of vHP injection of MCH on impulsive responding for food in the DRL task: a efficiency data during the training phase in DRL 20. (b–d; data were analyzed using Student’s two-tailed, paired t tests; n = 12). b Number of active lever presses during test phase (P = 0.02). c Number of pellets earned during test phase. d Efficiency in the DRL test phase (P = 0.008). e Schematic cartoon depicting methods for dual virus chemogenetic approach. The retroactively transported canine adenovirus 2 (CAV2 CRE) was used to deliver the transgene for cre recombinase to vHP projection neurons following direct injection into the vHP. A cre-dependent adeno-associated virus containing excitatory MCH DREADDs–mCherry transgene (AAV2 MCH DIO DREADDs) was injected into the LHA and ZI. f Representative images of fluorescent reporter localization in MCH neurons. g–j Effects of chemogenetic activation of MCH neurons that project to the vHP on impulsive responding for food in the DRL test session: g efficiency data during the training phase in DRL 20. (h–j; data were analyzed using Student’s two-tailed, paired t tests; n = 12), h number of active lever presses during DRL testing (P = 0.03), i number of pellets earned during DRL testing, and j efficiency during the DRL testing (P = 0.03). Data shown as mean ± SEM; scale = 50 µm; *P < 0.05. Source data are provided as a source data file