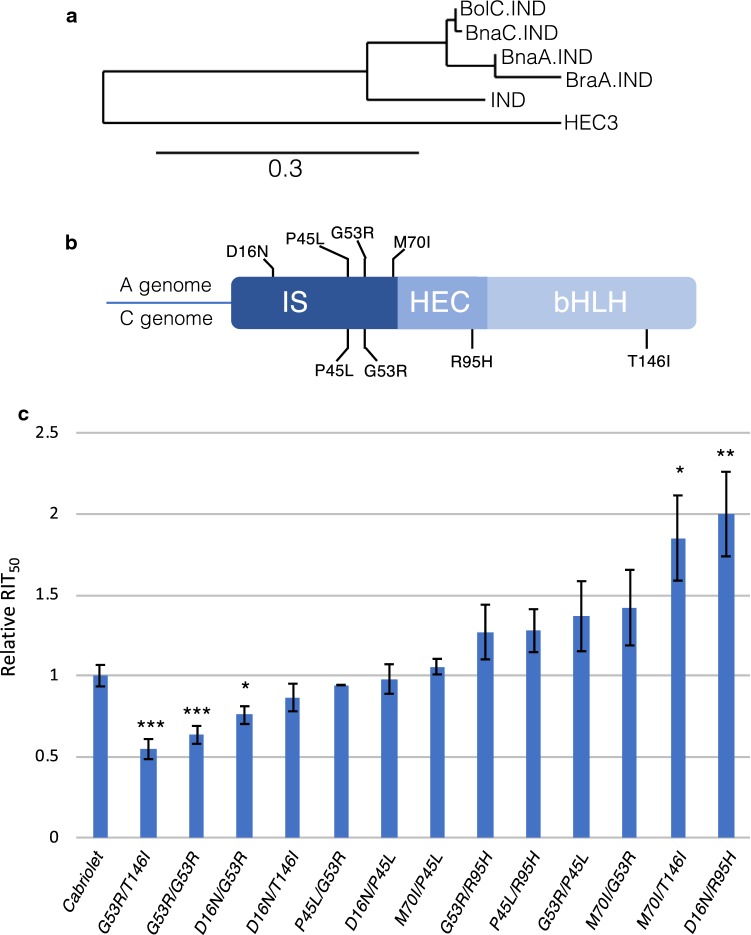
Fig. 3.
Identifying and characterising bna.ind mutants. a Phylogenetic analysis of Arabidopsis and Brassica IND protein sequences. HEC3 is HECATE3, which is the closest homologue of IND in Arabidopsis and used as an outgroup in this analysis. Scale bar indicates substitutions per site. b Schematic of IND protein divided into its three domains: the IND-specific (IS), HECATE (HEC) and basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) domains. Position and nature of missense mutations are shown with four from the A genome (top) and four from the C genome (bottom). c RIT half-lives (RIT50) plotted for the wild-type variety ‘Cabriolet’ and the combinations of bna.ind double mutants indicated in the graph with substitutions on the A genome in front of substitutions on the C genome. Error bars indicate standard error. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001