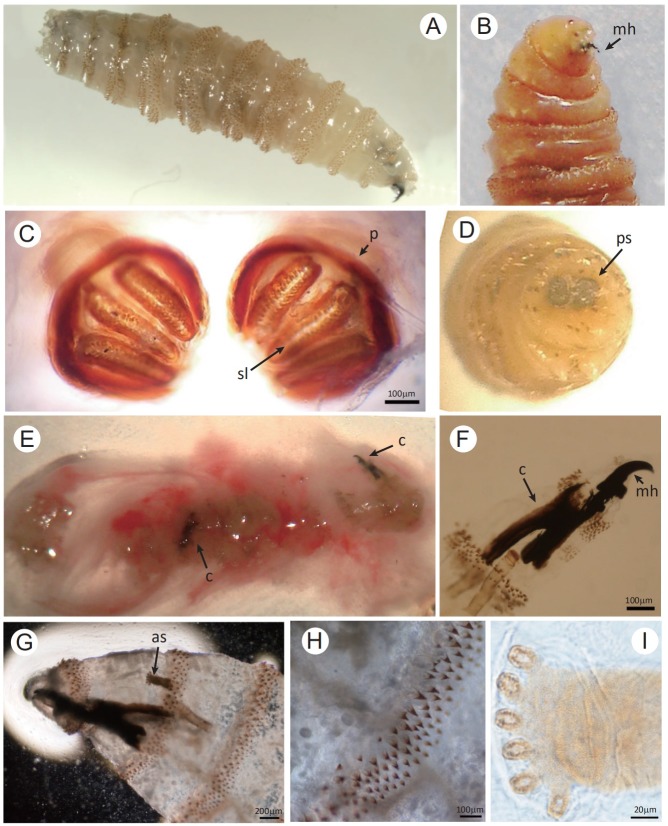
Fig 4. Morphology of the third-instar larva of Chrysomya bezziana.
(A, B) The third-instar is approximately 14 mm in length with strong mouth hooks (mh). (C) The posterior spiracles (ps) are observed with the spiracular slits (sl) slightly convergent and the peritreme (p) thick and incomplete. (D) Dissecting micrograph of the posterior spiracles (ps). (E-I) Two third-instar larvae were isolated from the discharge extruded from the patient’s skin lesion. (E) Showing the discharge containing two larvae with two black cephalopharyngeal skeletons (c), (F and G) the strong and robust mouth hook (mh), (G and I) the anterior spiracle (as) with palmate shape due to six papillae arranged in single row, and (H) the intersegmental spines with the single, darkened and tapered tips recurved toward the body. Bar: C, F and H = 100 μm; G = 200 μm; I = 20 μm.