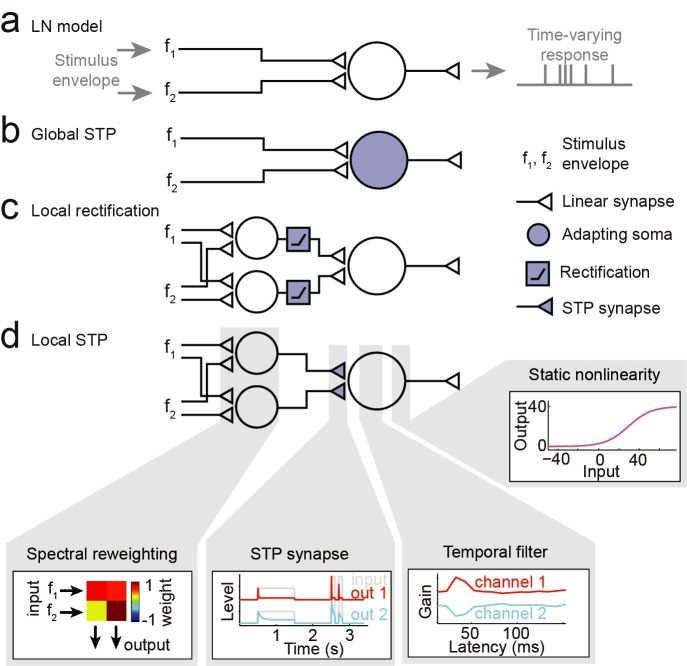
Fig 2. Alternative encoding models to describe auditory neural responses to vocalization-modulated noise.
A. The linear-nonlinear spectro-temporal receptive field (LN model) describes the time-varying neural response as a linear weighted sum of the preceding stimulus envelopes, followed by a static sigmoid nonlinearity to account for spike threshold and saturation. B. In the global short-term plasticity (STP) model, nonlinear STP (depression or facilitation) is applied to the output of the linear filter prior to the static nonlinearity. C. In the local rectification model, the input channels are linearly reweighted and then nonlinearly thresholded (rectified) prior to the linear temporal filter and static nonlinearity. D. In the local STP model, input channels are linearly reweighted, and then nonlinear STP (depression or facilitation) is applied to each reweighted channel, prior to the linear temporal filter and static nonlinearity. Gray boxes show example model parameters applied at each processing stage.