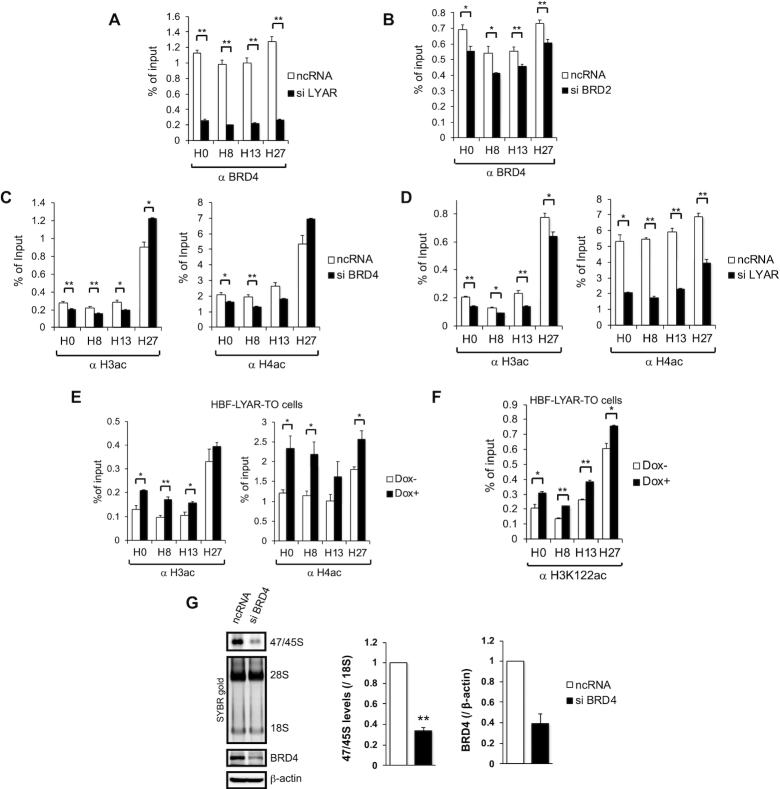
Figure 6.
LYAR and BRD2 assist the recruitment of BRD4 to rDNA (A, B) ChIP analysis of the binding of BRD4 to rDNA upon the knockdown of LYAR (A) or BRD2 (B). 293T cells were treated with ncRNA or an siRNA specific for LYAR (A) or BRD2 (B) for 72 h. These cells were subjected to ChIP analysis with an antibody against BRD4. The graphs show the amount of ChIPed DNA (% of input) relative to the number of rDNA loci indicated under each graph. Data represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (unpaired t-test). (C, D) ChIP analysis of the extent to which H3 or H4 is acetylated in 293T cells. The cells were treated with ncRNA or an siRNA specific for BRD4 (C) or LYAR (D) for 72 h. These cells were subjected to ChIP analysis with an antibody against H3ac or H4ac, as indicated. (E, F) ChIP analysis of the extent to which H3 or H4 is acetylated in HBF-LYAR-TO cells. The cells were treated with (Dox+) or without Dox (Dox–) for 24 h. These cells were subjected to ChIP analysis with an antibody against H3ac or H4ac (E), or H3K122ac (F). (G) Metabolic labeling (4-thiouridine) of newly synthesized 47/45S pre-rRNA in 293T cells upon BRD4 knockdown (siRNA) for 72 h. The pre-rRNA was biotinylated and then subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis and northern blotting. The signals for 47/45S pre-rRNA were detected by chemiluminescence. 28S and 18S rRNAs were used as loading controls (stained with SYBR gold). The graph shows the relative band intensities of biotin-labeled 47/45S pre-rRNA normalized to that of 18S rRNA. Data represent the mean ± SEM of four independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (paired t-test). Knockdown of BRD4 was confirmed by immunoblotting with anti-BRD4. β-actin was used as the loading control.