Figure 5.
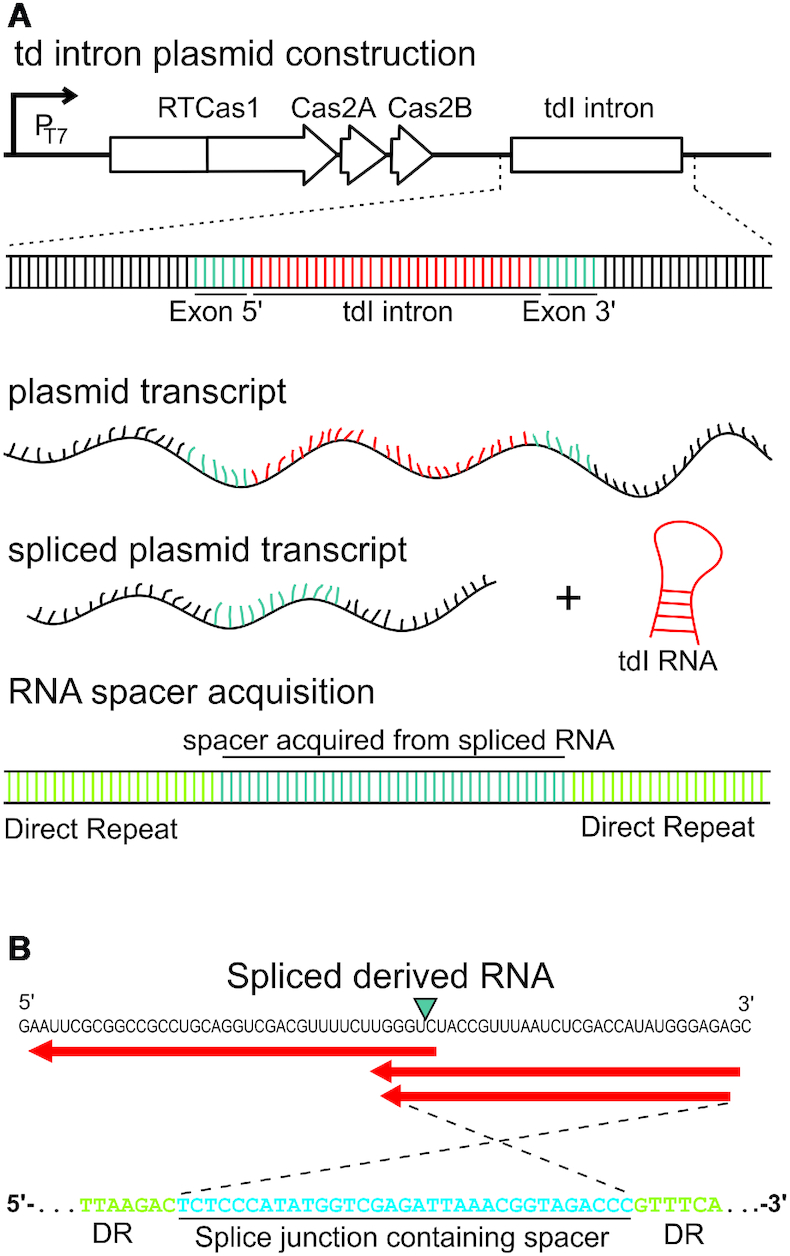
Spacer acquisition from RNA in the VVYJ016 type III-D system. (A) Schematic diagram of td intron-containing constructs. We determined whether the spacers originated from RNA, using a self-splicing transcript that produces an RNA sequence junction not encoded by DNA. Newly acquired spacers containing this exon junction may be considered to have been acquired from an RNA target. (B) RNA derived from the newly acquired exon junction-spanning spacer (blue). The splice site is indicated by a blue triangle. Red arrows indicate that the spacer are in the antisense orientation relative to the direction of transcription of the td intron. At the bottom, the highlighted sequence of one of the splice junction-containing spacers located in the CRISPR array is indicated.
