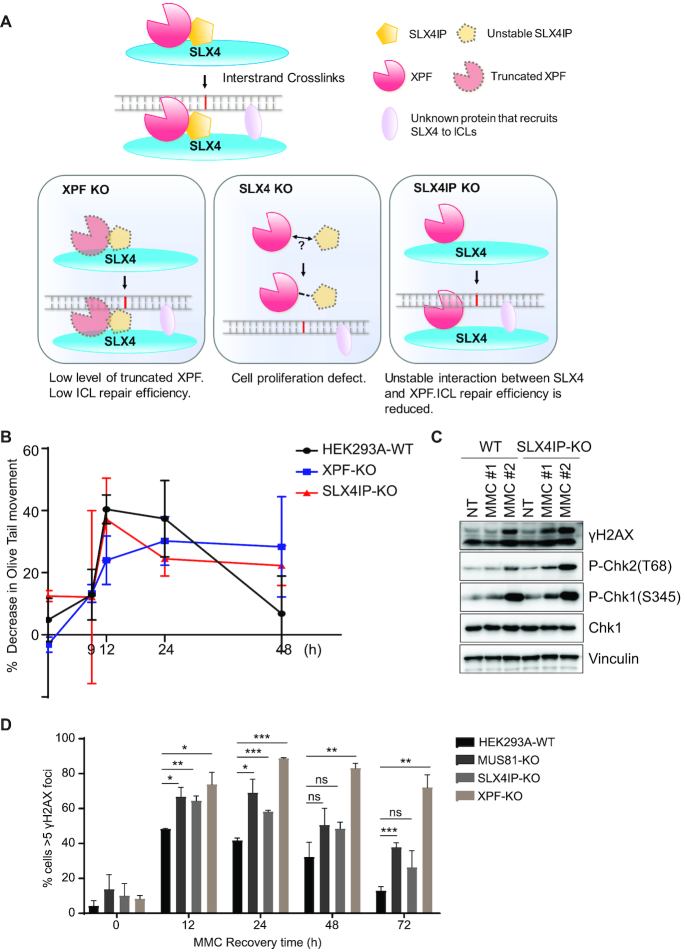
Figure 8.
Loss of SLX4IP reduces the repair efficiency of interstrand crosslink repair in vivo. (A) Working model of SLX4–XPF–ERCC1-SLX4IP interaction and function. Our current working hypothesis is that SLX4IP acts to promote the interaction between SLX4 and XPF–ERCC1, especially following DNA damage. This function of SLX4IP is critical for interstrand crosslink (ICL) repair. In our XPF-KO cells, truncated XPF was expressed only at low levels and SLX4IP protein was mostly degraded. Therefore, a very limited SLX4–XPF–ERCC1-SLX4IP complex formed and we observed severe ICL repair defects. When we overexpressed SLX4IP in these cells, the interaction between truncated XPF and SLX4 was enhanced, which suppressed the hypersensitivity of XPF-KO or XPF/SLX4IP-DKO cells to mitomycin C (MMC). We found that mAID-mediated downregulation of SLX4 also caused downregulation of SLX4IP protein, which may result in the failure of XPF–ERCC1 recruitment and diminished cell survival. As for SLX4IP-KO cells, SLX4 could still interact with XPF–ERCC1, but the complex was not stable; this was especially true following DNA damage, which resulted in reduced ICL repair efficiency. (B) Cells were treated with 1 μm MMC for 1 h and released for the indicated times. Samples were taken to detect the unhooking of ICL using a modified comet assay (please see the Material and Methods section for detailed description). DNA ICL is expressed as the percentage of decrease in Olive tail movement. Data are presented as the mean ± the standard error of the mean (n = 3). (C) HEK293A cells were mock-treated (Mock) or treated with MMC (either 1# 0.5 μg/ml MMC for 1 h and release for 24 h, or 2# 0.1 μg/ml MMC for 24 h). After treatment, whole-cell extracts were prepared and subjected to Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (D) HEK293A-WT, SLX4IP-KO, XPF-KO, and MUS81-KO cells were exposed to 0.5 μg/ml MMC for 1 h and allowed to recover after removal of the drug. Cells were then fixed with 3% paraformaldehyde and stained with an anti-γH2AX antibody. The percentages of cells with more than five γH2AX foci are shown. Data are presented as the mean ± the standard error of the mean (n = 3). Statistical analysis was performed using the Student's t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ns: not significant. P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. KO, knockout; WT, wild type.