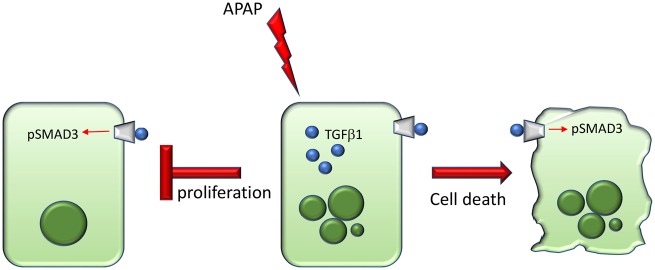
Figure 9.
Working schematic of effects of TGFβ1 signaling in APAP-treated mice. During APAP-induced hepatotoxicity, TGFβ1 is increased in injured and dying hepatocytes. Transforming growth factor beta 1 is able to bind the TGFβR1/TGFβR2 heterodimer on hepatocytes resulting in increased phosphorylation of pSMAD3. As a result of induction of TGFβ1 signaling, hepatocyte proliferation is inhibited and cell death is induced. The combination of these deleterious effects exacerbates APAP-induced liver injury.