Figure 6.
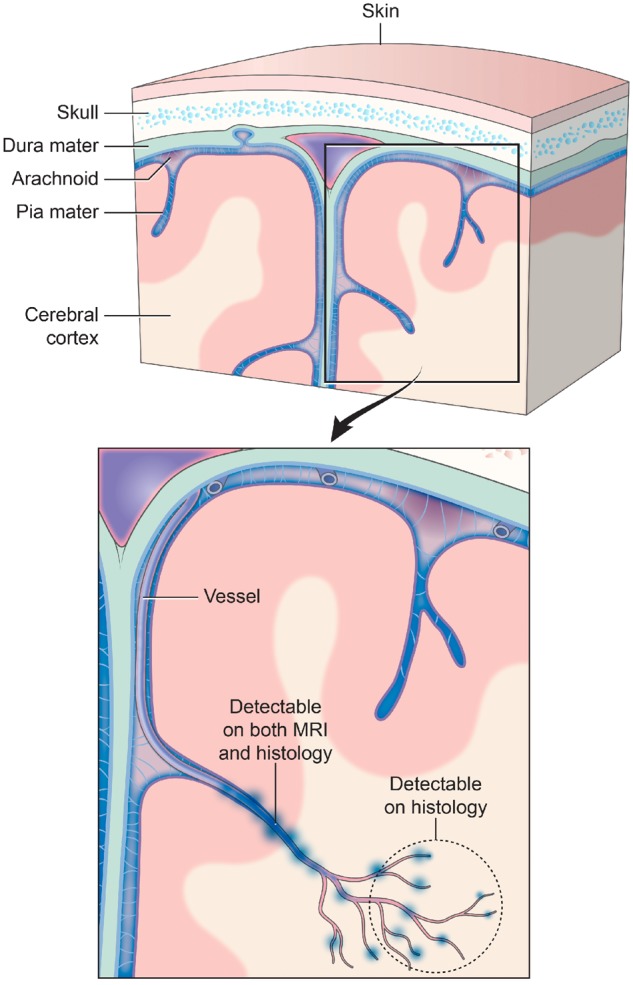
Traumatic vascular injury. Traditionally, TMBs have been described as markers for diffuse axonal injury. However, TMBs have not been characterized as a form of traumatic vascular injury. MRI and 3D histology identified an underlying pathology of TMBs to be an injury to not just a single vessel, but injury that extends to a vascular network. Injury to a large blood vessel causes iron deposition that is detectable on in vivo and ex vivo MRI (at 3 T and 7 T). Smaller vessels that form a broader vascular network with the larger vessels are missed in these magnetic resonance images. High-resolution 3D histology of iron deposits in macrophages identified more extensive vascular injury involving smaller vessels that connect to the larger injured vessel detected on MRI. The schematic above illustrates a model of this vascular injury pattern and potential levels of detection with MRI and histological approaches.
