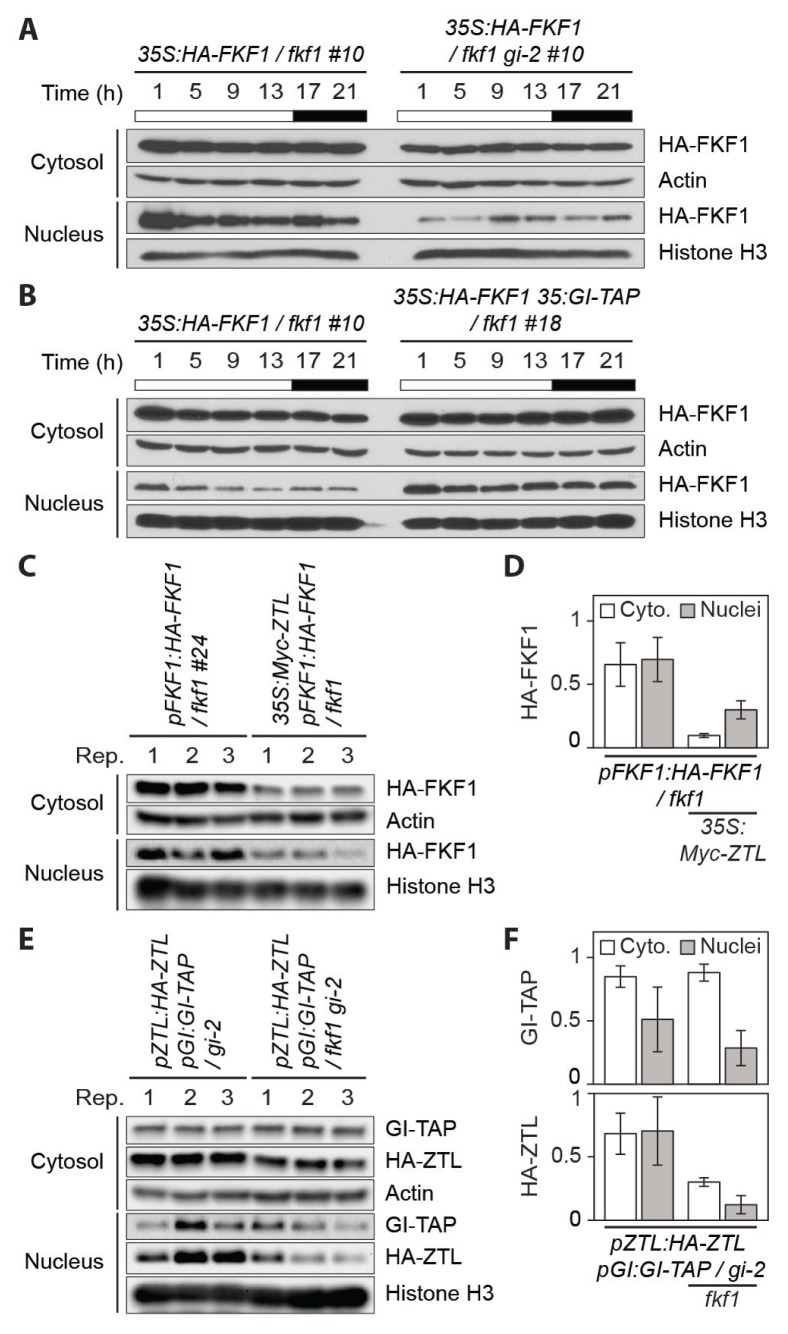
Fig. 1. GI regulates FKF1 protein abundance in long days.
(A and B) Immunoblot assays for daily expression profiles of FKF1 protein in the cytosol and the nucleus. The 35S:HA-FKF1 #10, 35S:HA-FKF1 / fkf1 gi-2 #10, and 35S:HA-FKF1 35S:GI-TAP / fkf1 #18 plants were grown for 10 days in long days. Effects of the gi mutation (A) and the GI overexpression (B) on FKF1 stability and translocation. Similar results were observed from two biological replicates. White and black bars represent the light and dark conditions, respectively. (C) FKF1 proteins in the cytosolic and nuclei fractions of the pFKF1:HA-FKF1 / fkf1 #24 and pFKF1:HA-FKF1 35S:Myc-ZTL / fkf1 plants grown for 10 days in long days and collected in the afternoon (ZT13). Rep., replication. (D) Quantification for the amounts of HA-FKF1 protein in the cytosol (abbreviated as Cyto.) and the nucleus with or without Myc-ZTL overproduction. (E) The effect of the fkf1 mutation on changes in the stability of GI and ZTL proteins between the cytosol and the nucleus. The pZTL:HA-ZTL pGI:GI-TAP / gi-2 and pZTL:HA-ZTL pGI:GI-TAP / fkf1 gi-2 plants grown in long days were harvested at ZT13 on day 10. (F) Quantification for the amounts of GI-TAP and HA-ZTL in the cytosol and the nucleus with or without the fkf1 mutation. Numbers in (C) and (E) represent each protein extract from three biological replicates. (D) and (F) Quantification data was calculated from the results of (C) and (E), respectively. Actin and Histone H3 antibodies were used for loading controls.