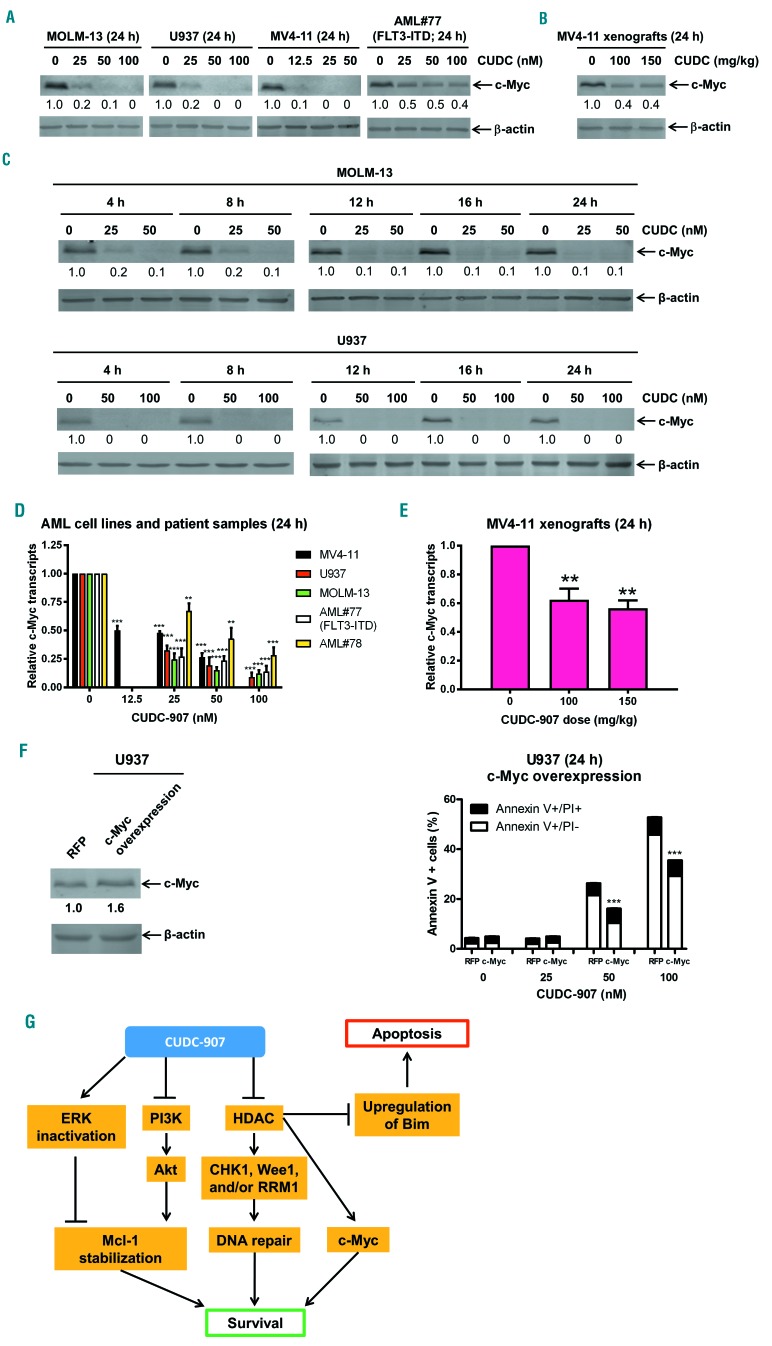
Figure 7.
CUDC-907 treatment downregulates c-Myc in acute myeloid leukemia cells. (A) Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell lines and primary AML patient sample AML#77 were treated with CUDC-907 for 24 h. Whole cell lysates were subjected to western blotting. Normalized densitometry measurements are shown. (B) the MV4-11 xenograft model was treated with a single dose of CUDC-907 21 days after cell injection. Bone marrow cells were harvested 24 h after treatment. Human cells were enriched and then whole cell lysates were subjected to western blotting. (C) MOLM-13 and U937 cells were treated with CUDC-907 for up to 24 h. Whole cell lysates were subjected to western blotting. (D) MV4-11, U937 and MOLM-13 AML cell lines and two primary AML patient samples were treated with 0-100 nM CUDC-907 for 24 h. Total RNA was isolated and c-Myc transcripts were determined by real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. (E) Cells obtained from the MV4-11 xenografts, which were treated with a single dose of CUDC-907, were enriched for human cells. Then total RNA was isolated and real-time RT-PCR performed to determine c-Myc transcripts. **P<0.01. (F) U937 cells were infected with Precision LentiORF c-Myc and red fluorescent protein (RFP) control lentivirus particles overnight, then washed and incubated for 24 h. The whole cell lysate from one aliquot of the cells was subjected to western blotting. The fold changes for the c-Myc densitometry measurements, normalized to β-actin and then compared to non-treated control (NTC), are indicated (left panel). The other aliquot of the cells was treated with CUDC-907 for 24 h and then subjected to annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) staining and flow cytometry analysis. ***P<0.001 (right panel). (G) Proposed mechanism of action of CUDC-907 treatment: (i) CUDC-907 inactivates ERK and inhibits PI3K resulting in reduced Mcl-1 expression; (ii) CUDC-907 inhibits histone deacetylases (HDAC) which downregulates CHK1, Wee1, and/or RRM1, reducing DNA repair; (iii) CUDC-907 inhibits HDAC decreasing c-Myc; and (iv) CUDC-907 inhibits HDAC which upregulates Bim. The foregoing molecular changes lead to apoptosis.