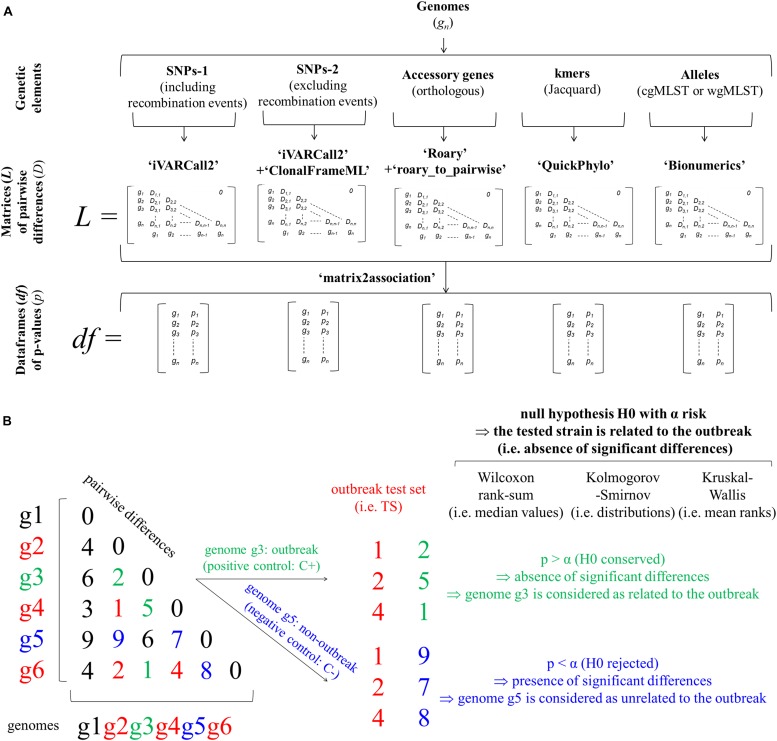
FIGURE 2.
Workflows implementing non-parametric tests to assess statistical differences of pairwise differences of genomic features at the core (i.e., approaches ‘SNPs-1,’ ‘SNPs-2,’ and ‘cgMLST’), accessory (i.e., approaches ‘genes’) and pangenome (i.e., approaches ‘kmers’ and ‘wgMLST’) scales in order to investigate food poisoning outbreaks (A) and statistical approaches implementing non-parametric tests (i.e., WS, KS, and KW) comparing pairwise differences of genomic features during a foodborne outbreak (FBO) investigation (B). The approaches ‘SNPs-1,’ ‘SNPs-2,’ ‘genes,’ ‘kmers,’ ‘cgMLST,’ and ‘wgMLST’ were performed with the workflows iVARCall2 with or without ClonalFrameML, ARTWork-Roary, ARTWork-QuickPhylo, and BioNumerics (Applied Maths), respectively. The ‘SNPs’ approaches were performed including (i.e., ‘SNPs-1’) or excluding (i.e., ‘SNPs-2’) SNPs from recombination events identified with ClonalFrameML. The R script ‘matrix2association’ estimates statistical differences between two lists of pairwise differences existing across genomes known to be involved in a studied outbreak (i.e., outbreak test set: TS) and between these genomes and a tested genome (i.e., outbreak control C+ or non-outbreak control C–) in order to assign (i.e., absence of statistical differences: H0 conserved), or not (i.e., presence of statistical differences: H0 rejected) this tested genome to the outbreak of interest.