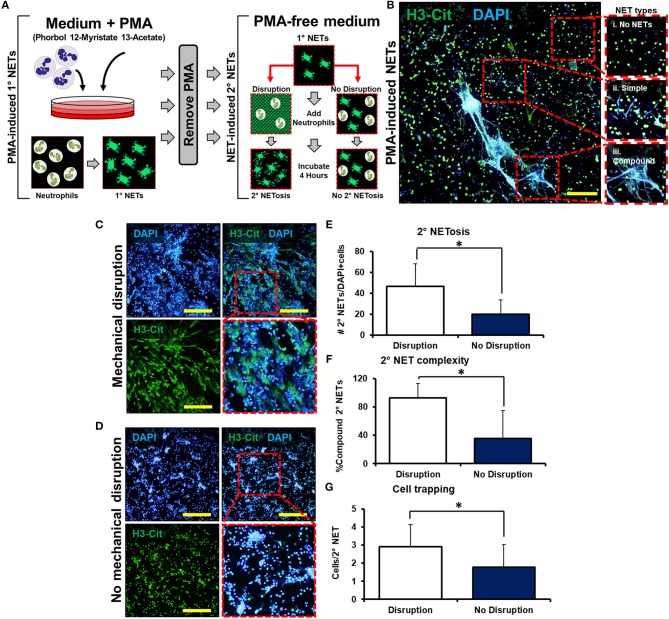
Figure 2.
Mechanically disrupted NETs induce NETosis. (A) In vitro experimental set-up to evaluate whether mechanical disruption of NETs can induce NETosis; (B) Representative images from PMA-induced NETs to demonstrate types of NETs; (C) 2° NETs with mechanical disruption of 1° NETs; (D) 2° NETs without mechanical disruption of 1° NETs; (E) Number of 2° NETs normalized to the number of DAPI+ cells per hpf (46.6 vs. 20.2, p < 0.05); (F) Number of compound 2° NETs normalized to the number of all NETs per hpf (92.7 vs. 35.8, p < 0.05); (G) Number of DAPI+ nuclei normalized to the number of 2° NETs per hpf (2.9 vs. 1.8, p < 0.05). Scale bars are 200 μm. All in vitro studies had n = 15 hpf/group. *p < 0.05.