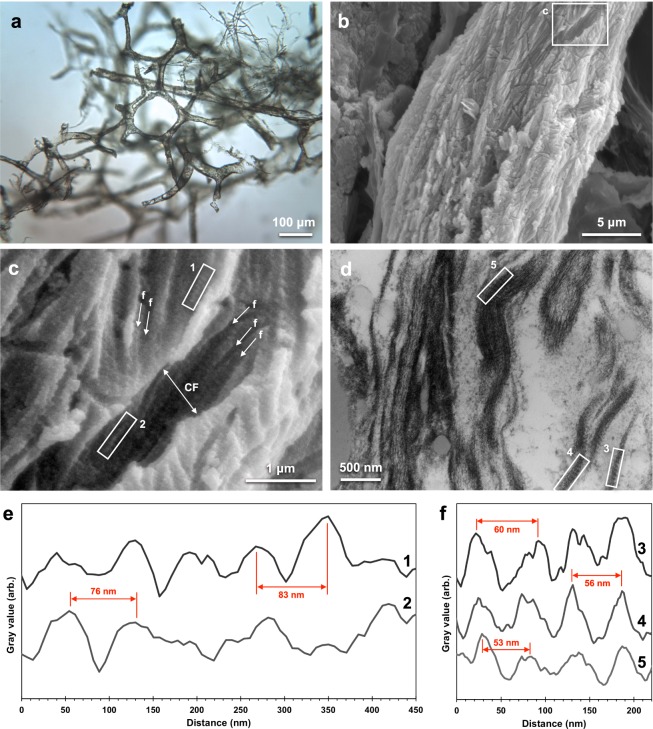
Figure 2.
Microscopy images of T. rex vascular tissue and associated analysis of fibrillar collagen banding. (a) Transmitted VLM of T. rex soft tissue shows an extensive network of hollow, pliable, vascular structure and typical brown hue. (b) SEM image of the surface of a vessel. (c) Magnified image of (b) detailing features consistent with collagen fibre bundles (collagen fibril, “f”; collagen fibre, “CF”). Average fibril width was measured as 110 nm, and average fibre width, 1.0 μm. (d) TEM image of fibrous features observed in a longitudinal vessel cross-section. Intensity profiles of banded texture in (e) boxes 1 and 2 in c and (f) boxes 3, 4, 5 in (d) with example peak-to-peak distances (SEM average, ~74 nm; TEM, ~56 nm) called out in red. See Fig. S6 for precise d-spacing values determined using SAXS. For comparison to a modern blood vessel network in bone, see Fig. 5b of ref.39.