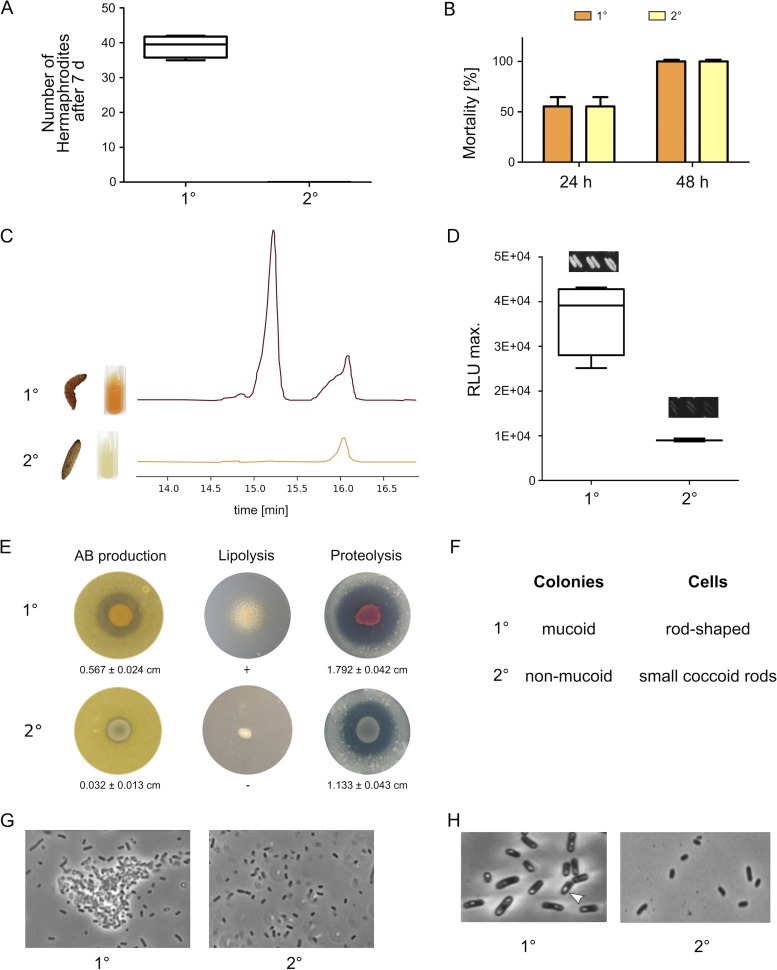
FIG 1.
Phenotypic comparison of P. luminescens DJC 1° and 2° cells. (A) Nematode bioassay. Fifty axenic Heterorhabditis bacteriophora IJs were spotted on 1° or 2° cells grown on lipid agar plates. After 7 days the number of developed hermaphrodites was counted. (B) Pathogenicity assay. Approximately 2,000 of the 1° or 2° cells were injected into 10 G. mellonella larvae each. Mortality was monitored over 48 h. (C) Pigmentation of both phenotypic cell forms was visually monitored over 5 days, and anthraquinone production was quantified from culture supernatant extracts via HPLC. (D) Bioluminescence of 1° and 2° cells was monitored over 24 h using a luminescence plate reader. Additionally, single colonies were streaked, and light production was visually analyzed by taking pictures with 5 min of exposure time. (E) To test for antibiotic production both 1° and 2° cells were spotted onto B. subtilis germ-agar plates. Furthermore, lipolytic or proteolytic activity was tested by spotting both phenotypic cell forms onto Tween agar or skim milk agar plates, respectively. (F) The colony morphology of both cell forms was analyzed by streaking single colonies with a toothpick. The shape of the cells as well as formation of cell clumps (G) and crystal inclusion proteins (H) was investigated via phase-contrast microscopy. Error bars represent standard deviations of three independently performed experiments.