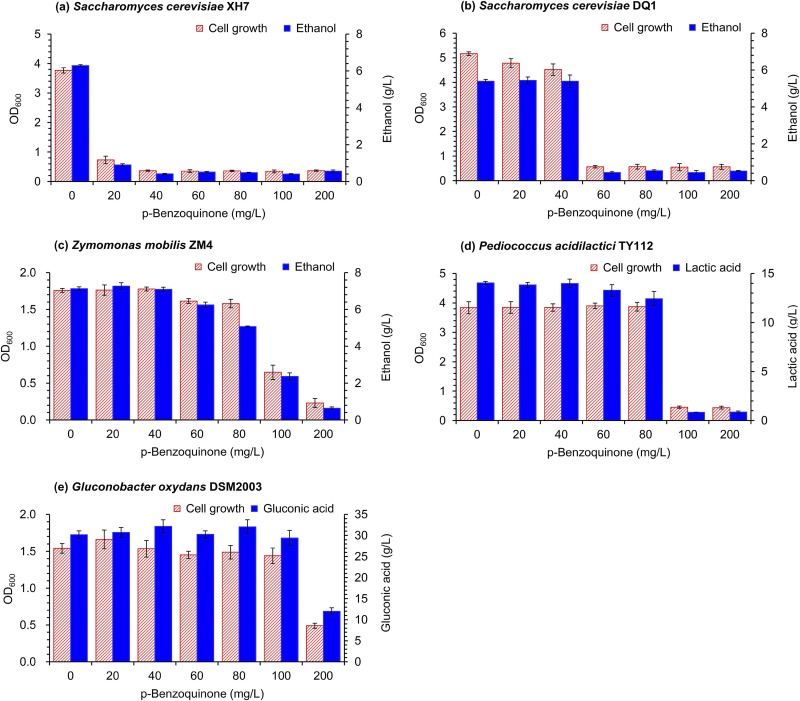
FIG 2.
Inhibition of p-benzoquinone (BQ) on cell growth and product fermentation of the five different yeasts and bacterial strains. (a) Engineered S. cerevisiae XH7 with glucose and xylose cofermentation into ethanol. (b) Thermotolerant strain S. cerevisiae DQ1 for ethanol fermentation. (c) Wild Z. mobilis ZM4 for ethanol fermentation. (d) Engineered P. acidilactici TY112 for l-lactic acid fermentation. (e) Wild G. oxydans DSM2003 for gluconic acid fermentation. The cell growth and product generation were measured at 12 h for all of the five strains. Conditions were as follows: 10% (vol/vol) inoculum size, 30°C, and 150 rpm for S. cerevisiae XH7 and S. cerevisiae DQ1; 30°C in static-state culture for Z. mobilis ZM4; 42°C and 150 rpm for P. acidilactici TY112; and 30°C and 220 rpm for G. oxydans DSM2003. Error bars represent two standard deviations. OD600, optical density at 600 nm.