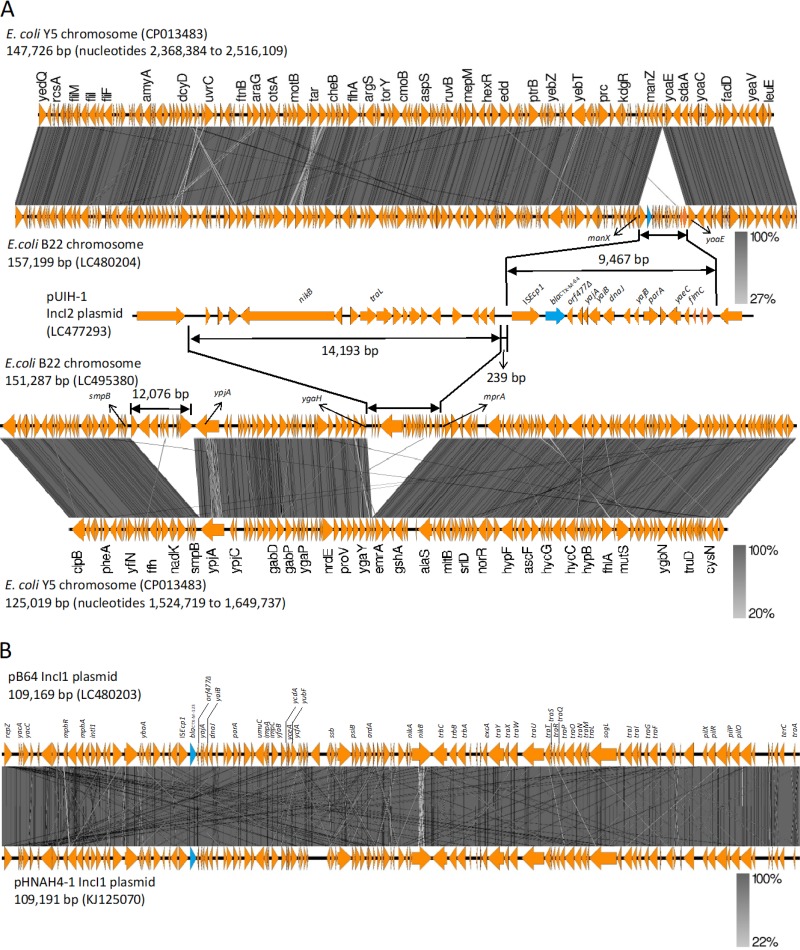
FIG 1.
Schematic representation of the chimeric genes. (A) Genome alignments of E. coli B22, including the 9,467-bp sequence of ISEcp1-blaCTX-M-64-orf477Δ-yajA-yaiB-orf1-dnaJ-orf2-yajB-parA-orf3-yaeC-flmC-orf4-orf5-orf6 (GenBank accession number LC480204) with E. coli Y5 (CP013483), and of E. coli B22, including 14,193-bp sequence immediately upstream region of the ISEcp1-blaCTX-M-64 (GenBank accession number LC495380) with E. coli Y5 (CP013483), and comparison of genetic environment flanking blaCTX-M-64 in E. coli B22 to that of plasmid pUHI from S. sonnei (GenBank accession number LC477293). (B) Sequence comparison between plasmid pB64 carrying blaCTX-M-123 (GenBank accession number LC480203) and pHNAH4-1 (KJ125070). The arrows show the translation orientation of the coding genes. Figure was generated using EasyFig (http://mjsull.github.io/Easyfig/).