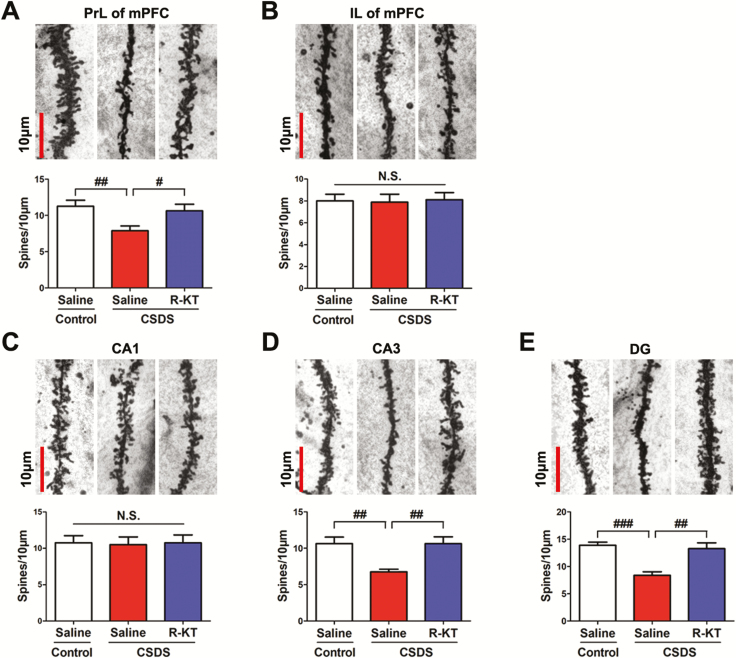
Figure 2.
Rapid effects of (R)-ketamine on the decreased dendritic spine density in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus in susceptible mice after CSDS. (A-E) Dendritic spine density in the PrL and IL regions of the mPFC, CA1, CA3, and DG of the hippocampus. The bar is 10 μm. (A) PrL region of mPFC (1-way ANOVA, F2,21 = 4.825; P = 0.019). (B) IL region of mPFC (1-way ANOVA, F2,21 = 0.027; P = 0.973). (C) CA1 of hippocampus (1-way ANOVA, F2,21 = 0.019; P = 0.982). (D) CA3 of hippocampus (1-way ANOVA, F2,21 = 8.144; P = 0.002). (E) DG of hippocampus (1-way ANOVA, F2,21 = 14.070; P < 0.001). The values represent the mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 8/group). #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, and ###P < 0.001, compared with saline-treated CSDS-susceptible mice. Abbreviations: ANOVA, analysis of variance; CSDS, chronic social defeat stress; DG, dentate gyrus; IL, infralimbic; mPFC, medial prefrontal cortex; N.S., not significant; PrL, prelimbic; R-KT, (R)-ketamine.