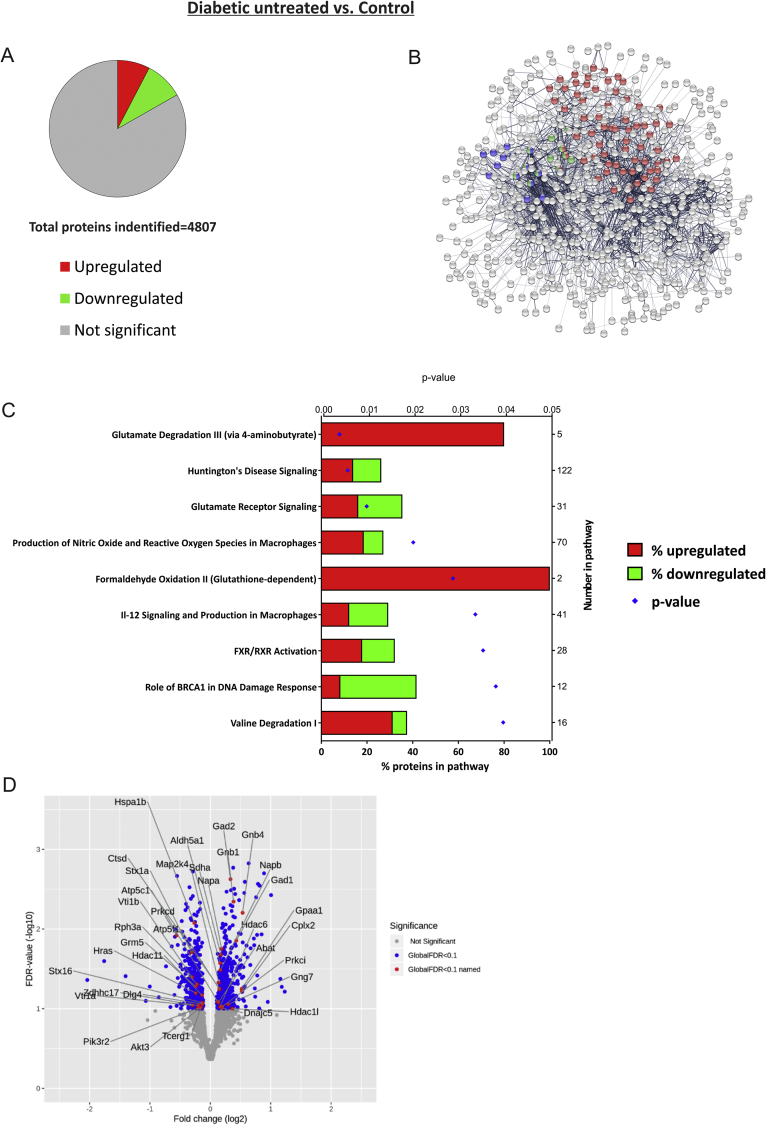
Figure 5.
Proteomic pathway analysis revealed dysregulation in glutamatergic, oxidative and nitrative stress and inflammatory pathways in the diabetic rat hippocampus. A) Of the 4807 identified and quantified proteins 17% were significantly altered (FDR<10%) in the hippocampus of diabetic (n = 6) vs. control (n = 4) rats (Study 4; up-regulated (red) or down-regulated (green)). B) STRING Network analysis highlights interaction networks for significantly altered proteins and the proteins in most significant KEGG pathways are represented as colored nodes (Red: ‘Metabolic pathways’, Blue: ‘Glutamatergic synapse’ and Green: ‘GABAergic synapse’). C) Ingenuity Pathway Analysis reveals 9 significantly overrepresented pathways organized by P value (shown on top x-axis); the bars show percentage of proteins in each pathway (bottom x-axis) that are up-regulated (red) or down-regulated (green), total number of proteins within each named pathway is shown on the right-hand Y axis. D) Volcano plot showing the distribution of total protein expression arranged by log2-fold change and FDR. Significantly changed proteins (FDR<10%) are colored blue and the proteins from the top 2 canonical pathways in the IPA analysis (C: “Glutamate degradation III” and “Huntington's Disease signaling”) are labeled in red (as their gene names).