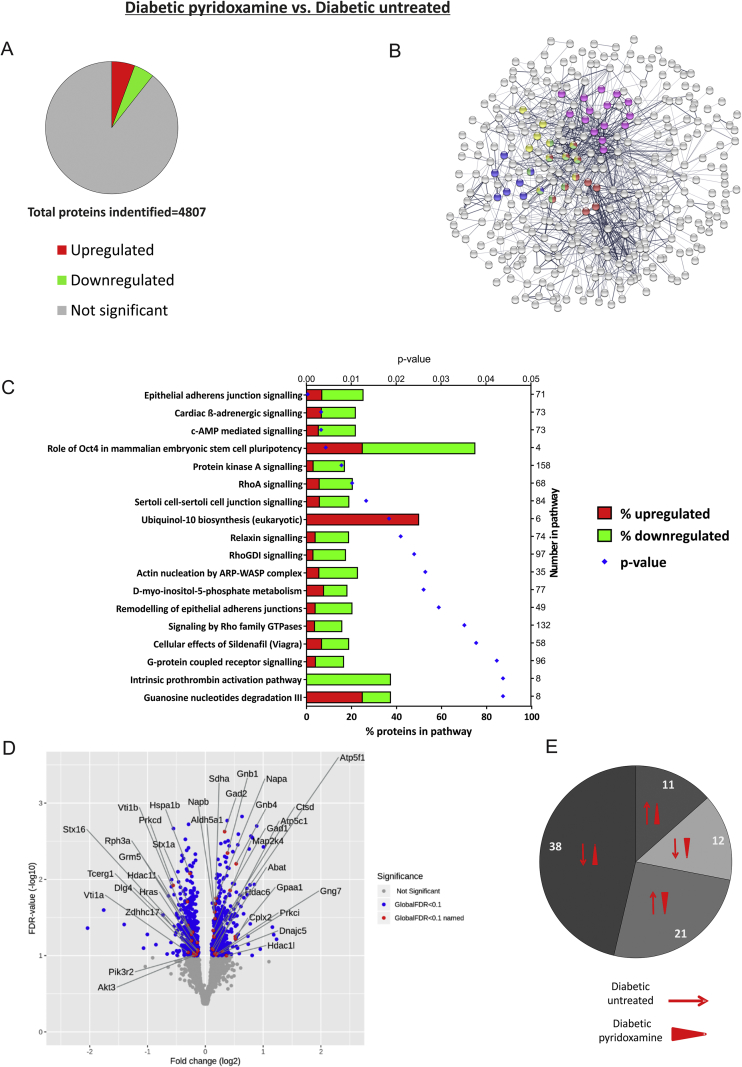
Figure 6.
Proteomic pathway analysis reveals alterations in cytoskeletal-associated proteins and signal transduction pathways in the hippocampus of pyridoxamine-treated diabetic rats. A) 511 of the identified proteins were significantly up-regulated (red) and down-regulated (green) in the hippocampus of pyridoxamine-treated (n = 6) compared to untreated-diabetic rats (n = 6) rats (Study 3). B) STRING Network analysis highlights networks and association for significantly altered proteins and proteins in most significant KEGG pathways are represented as colored nodes (Red: “Morphine addiction”, Blue: “Synaptic vesicle cycle”, Green: “Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling’, Yellow: “Glutamatergic synapse”, Pink: “Regulation of actin cytoskeleton”). C) Ingenuity Pathway Analysis highlights 18 significantly changed pathways organized by P value (shown on top x-axis); the bars show percentage of proteins in pathway (bottom x-axis) that are up-regulated (red) and down-regulated (green), total number of proteins within each named pathway is shown on right-hand Y axis. D) Volcano plot shows distribution of total protein expression by log2-fold change and FDR. Significantly changed proteins (FDR<10%) are colored blue, and proteins from the top canonical pathway (C: “Epithelial adherens junction signaling”) are labeled in red (as their gene names). E) Pie chart shows the expression profiles of the 82 proteins that were significantly changed in both control vs diabetic and diabetic-untreated vs. diabetic-pyridoxamine datasets. Those up or down-regulated in diabetes compared to controls are shown as thin red arrow and those up- or down-regulated in pyridoxamine-treated diabetic rats compared to untreated-diabetic rats are shown as red arrowheads (e.g. 21 proteins were up-regulated in diabetes and down-regulated in pyridoxamine treated rats).