Figure 1.
Macrophages Were Activated in the Lung Tissues of ALI Mice
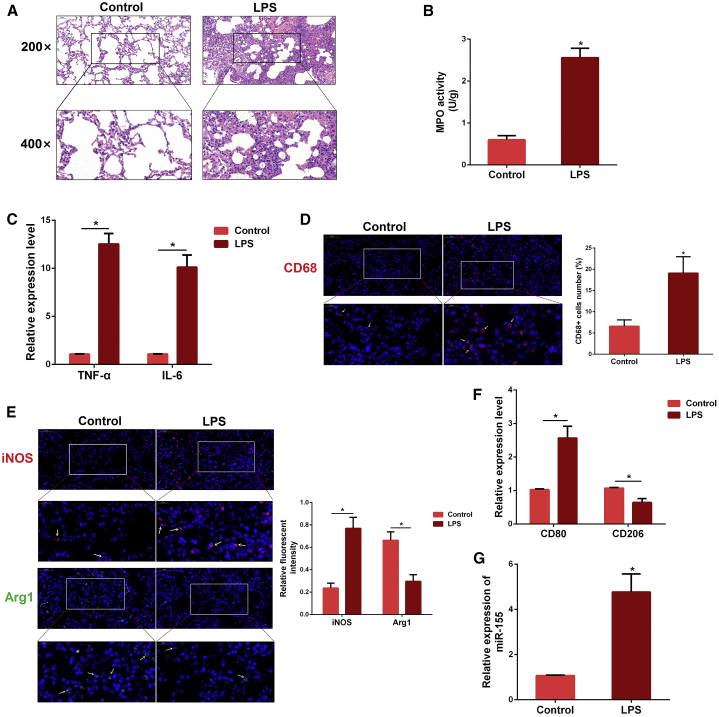
(A) Histopathological analysis of lung tissues. Mice were intraperitoneally (i.p.) injected with LPS for 12 h, and the degree of lung inflammation was assessed with H&E staining (n = 3 per group). (B) Infiltration of inflammatory cells into the lung tissues was measured by MPO activity (n = 4 per group). (C) The levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 were detected by qPCR (n = 3 per group). GAPDH was used as an endogenous control. (D) Sectioned tissues were stained with anti-CD68 antibody to identify the number of macrophages in lung tissues (n = 3 per group). The CD68-positive macrophages were normalized to DAPI-positive cells. (E) Immunofluorescence intensity of M1 and M2 macrophages in lung tissues (n = 3 per group). iNOS (M1, green) or Arg1 (M2, red). (F) The expression of CD80 and CD206 was determined by qPCR. GAPDH was used as an endogenous control (n = 3 per group). (G) The miR-155 expression was detected in the lung tissues of LPS-treated mice by qPCR (n = 4 per group). U6 snRNA was used as an endogenous control. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05.