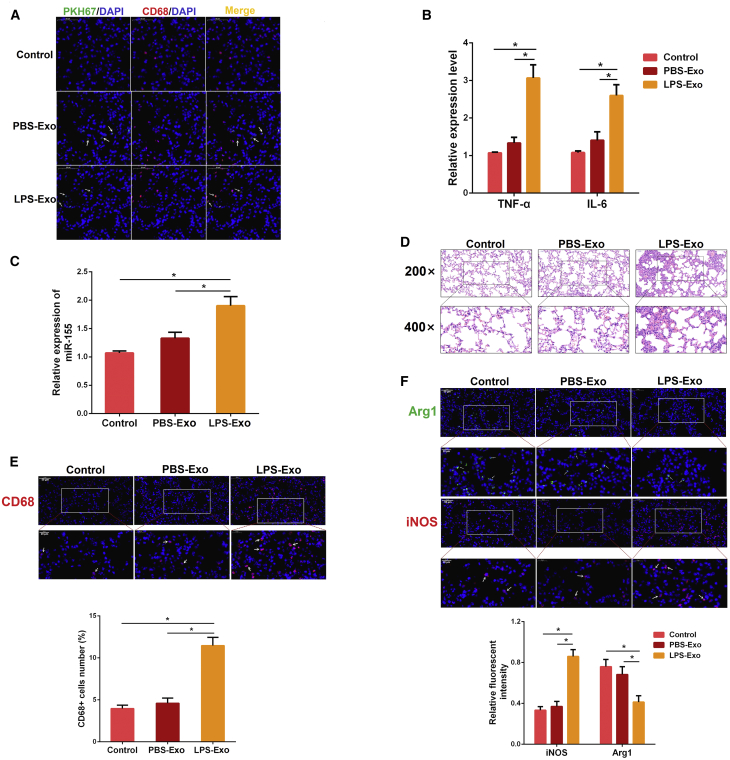
Figure 3.
Injection of Serum Exosomes from ALI Mice Induces Lung Inflammation in Naive Mice
(A) Serum exosomes from each experimental group (control and ALI) and PBS as a control were labeled with green fluorescent dye and injected into naive mice via tail vein. After 6 h, the lung tissues were stained with anti-CD68 antibody (macrophages, red) and DAPI (nucleus, blue) (n = 3 per group). Pictures were obtained by fluorescence microscopy. (B) The levels of TNF-α and IL-6 were detected by qPCR 24 h after exosome injection (n = 3 per group). GAPDH was used as an endogenous control. (C) The miR-155 expression was measured by qPCR (n = 4 per group). U6 snRNA was used as an endogenous control. (D) Representative images of lung histology stained with H&E (n = 3 per group). (E) Sectioned tissues were stained with anti-CD68 antibody to identify the number of macrophages in lung tissues. The CD68-positive macrophages were normalized to DAPI-positive cells (n = 3 per group). (F) Immunofluorescence intensity of M1 and M2 macrophages in lung tissues (n = 3 per group). iNOS (M1, green) or Arg1 (M2, red). PBS-Exo and LPS-Exo represent serum exosomes isolated from control and ALI mice, respectively. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05.