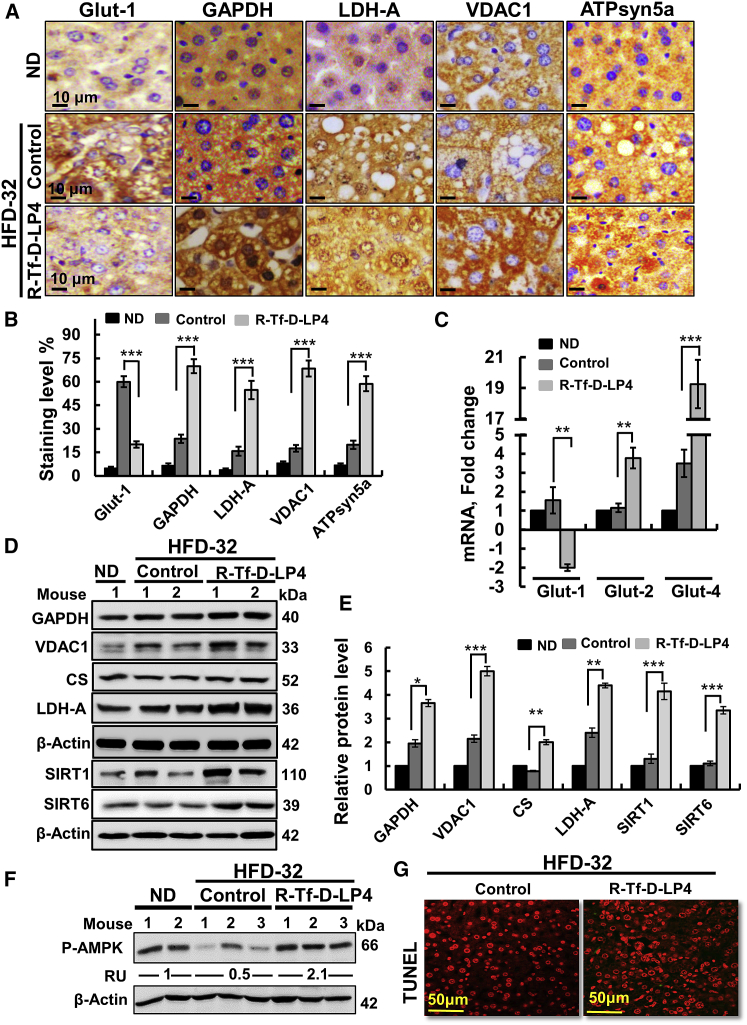
Figure 4.
R-Tf-D-LP4 Peptide Treatment of HFD-32-Fed Mice at the Steatosis Stage Altered the Expression of Metabolism-Related Enzymes
(A) Representative IHC staining of proteins mediating glucose transport (Glut-1), glycolysis (GAPDH, LDH-A), mitochondria metabolite transport (VDAC1), and OXPHOS (ATP synthase-5a) in liver sections from ND-fed mice and HFD-32-fed mice with and without peptide treatment. (B) Quantification of IHC staining intensity. (C) qRT-PCR analysis of the glucose transporters Glut-1, Glut-2, and Glut-4 in the 3 mouse groups. Immunoblot (D) and quantitative analysis (E) of metabolism-related enzymes and SIRT1 and SIRT6. Results are means ± SEM (n = 3–5; **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001). (F) Immunoblot and quantitative analysis of phosphorylated AMPK (p-AMPK). RU represents relative unit. (G) Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining of liver sections from HFD-32-fed and HFD-32-fed, peptide-treated mice. β-actin served as a loading control.