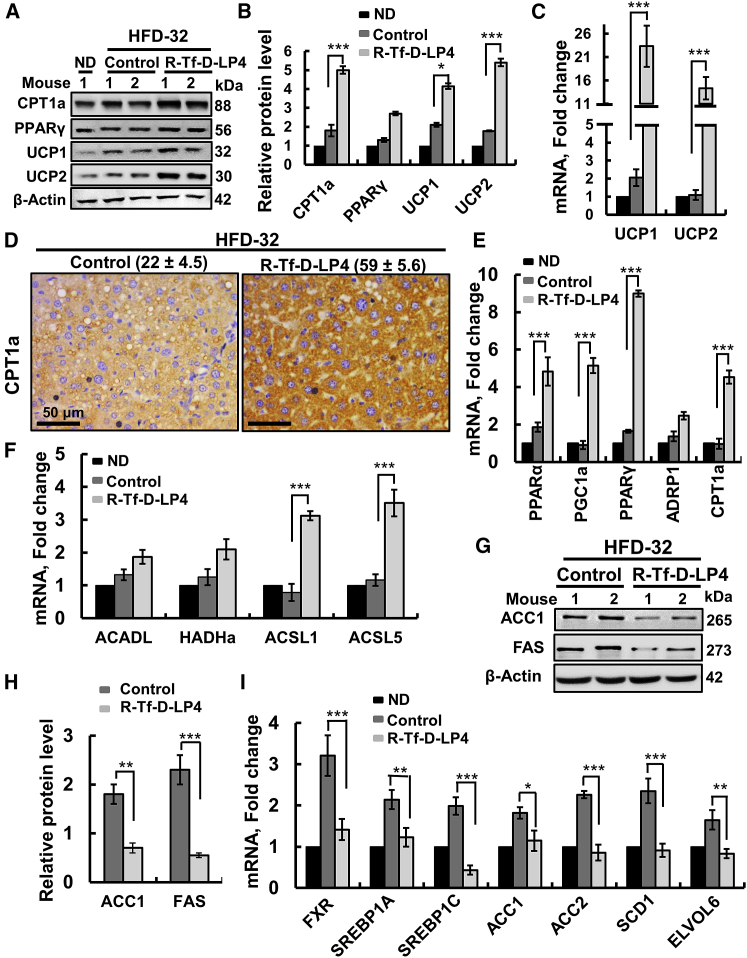
Figure 8.
R-Tf-D-LP4 Peptide-Mediated Lipid Metabolism Reprogramming in HFD-32 Mice at the NASH Stage
Proteins extracted from liquid nitrogen-frozen liver obtained from HFD-32-fed mice untreated or peptide treated (14 mg/kg) at the NASH stage were subjected to immunoblotting (A) and quantitative protein analysis (B). (C) UCP1 and UCP2 mRNA levels were analyzed in mRNA isolated from frozen livers by qRT-PCR of chow-fed mice (black bars) and untreated (dark gray bars) or peptide-treated HFD-32-fed mice (light gray bars). (D) IHC of CPT1a in liver sections from HFD-32-fed mice untreated (control) or treated with R-Tf-D-L4 peptide, with the relative intensity (n = 3 liver sections) presented in parentheses. (E and F) qRT-PCR analysis of mRNA levels of proteins, factors, and co-activators involved in lipid metabolism and regulation in chow-fed mice (black bars) and HFD-32-fed mice untreated (dark gray bars) or treated with R-Tf-D-LP4 peptide (light gray bars). Proteins associated with lipid metabolism (E) or involved in fatty acid transport (F). Immunoblot (G) and quantitative analysis (H) of proteins related to lipid biosynthesis in livers from HFD-32-fed mice untreated (dark gray bars) or treated with R-Tf-D-LP4 peptide (light gray bars). β-actin served as a loading control. (I) mRNA levels of lipid synthesis-associated proteins in chow-fed mice (black bars) and HFD-32-fed mice untreated (dark gray bars) or treated with R-Tf-D-LP4 peptide (light gray bars). Results are mean ± SEM (n = 3–5; *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001).