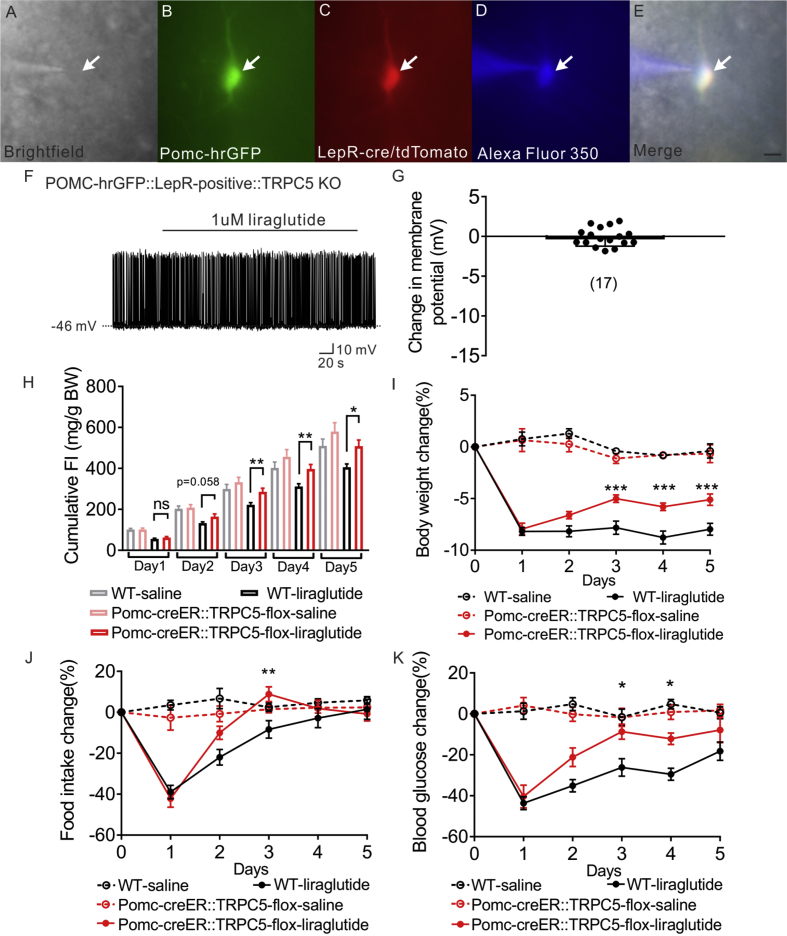
Figure 3.
Liraglutide depolarizes LepR expressing POMC neurons via TrpC 5 subunits. (A) Brightfield illumination of POMC-hrGFP::Lepr-cre::tdtomato neuron from POMC-hrGFP::Lepr-cre::tdtomato::TrpC5 KO mice. (B) and (C) The same neuron under FITC (hrGFP) and Alexa Fluor 594 (tdtomato) illumination. (D) Complete dialysis of Alexa Fluor 350 from the intracellular pipette. (E) Merge image illustrates colocalization of hr-GFP, tdtomato, and Alexa Fluor 350 indicative of LepR expressing (white arrows) POMC neurons. (F) Representative trace showing that liraglutide fails to induce a depolarization in a POMC-hrGFP::Lepr-cre::tdtomato::TrpC5 KO (green/red) neuron. (G) Histogram summarizing the acute effect of liraglutide on the membrane potential of LepR expressing POMC neurons which deleted of TrpC5. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Plots show the changes in cumulative food intake (H), body weight (I), daily food intake (J), and blood glucose (K) with daily injection of liraglutide on both litter mates control and POMC-creER::TrpC5-flox mice. Data are from male chow-fed mice. Number of mice studied for each group equals or above 5. Unpaired t-test compared to controls. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.