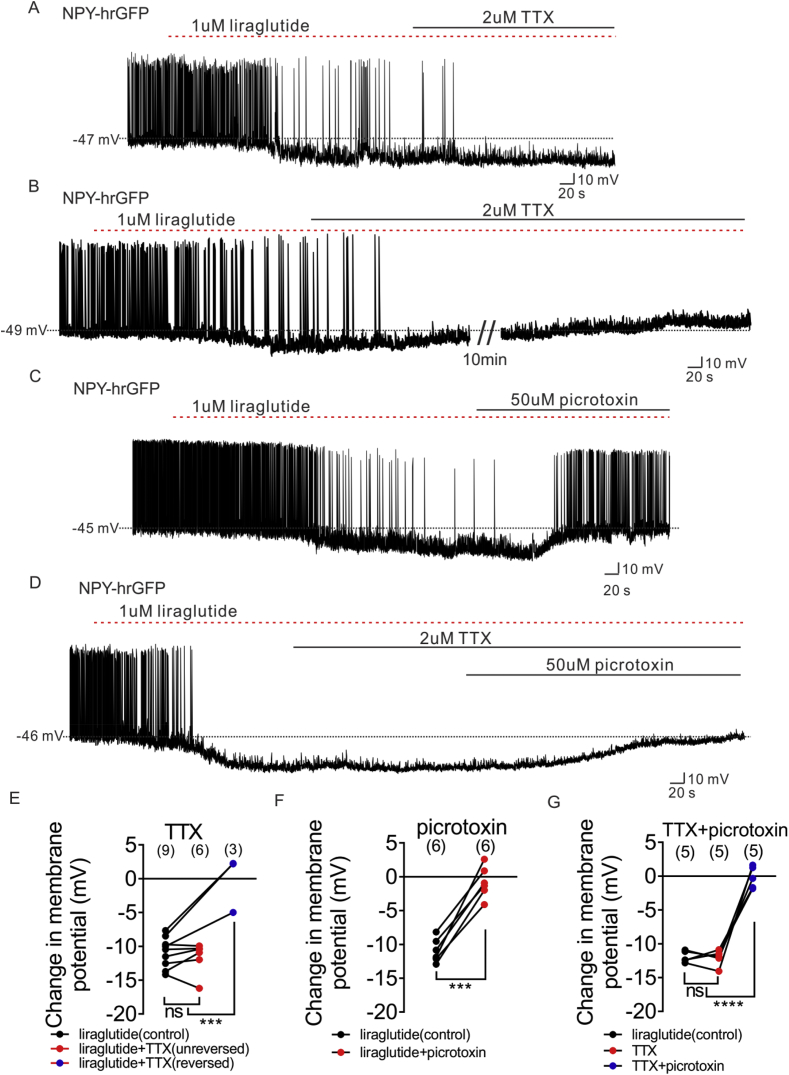
Figure 6.
Liraglutide hyperpolarizes NPY neurons via both pre-synaptic GLP1 receptor and post-synaptic GABAA receptor. (A) Representative trace showing that TTX (2 μM) does not prevent the liraglutide (1 μM)-induced hyperpolarization of NPY neurons. (B) Representative trace showing that TTX (2 μM) blocked the liraglutide (1 μM)-induced hyperpolarization of NPY neurons. (C) Representative trace showing that picrotoxin (50 μM) reversed the liraglutide (1 μM)-induced hyperpolarization of NPY neurons. (D) Representative trace showing that picrotoxin (50 μM) reversed the liraglutide (1 μM)-induced hyperpolarization of NPY neurons in which TTX (2 μM) does not blocked the liraglutide-induced effect. (E) Histogram summarizing the acute effect of liraglutide and followed by TTX (2 μM) administration on the membrane potential of arcuate NPY neurons (black: liraglutide, red: TTX does not block the liraglutide-induced effect, blue: TTX blocked the liraglutide-induced effect). (F) Histogram summarizing the acute effect of liraglutide and followed by picrotoxin (50 μM) administration on the membrane potential of arcuate NPY neurons (black: liraglutide, red: picrotoxin reversed the liraglutide effect). (G) Histogram summarizing the acute effect of liraglutide and followed by picrotoxin (50 μM) administration on the membrane potential of arcuate NPY neurons, in which TTX (2 μM) does not block the liraglutide-induced effect. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, unpaired & paired t-test were used to compare the significance.