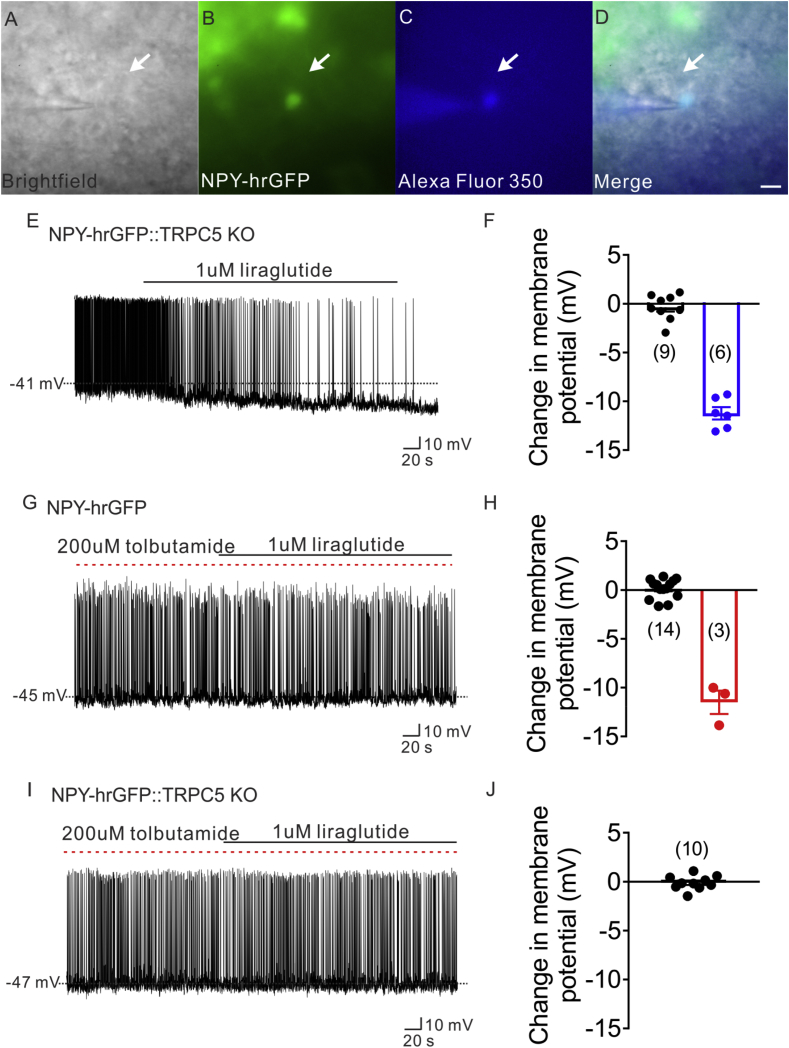
Figure 7.
ATP-sensitive potassium channel (K-ATP) and TrpC 5 subunits were involved in liraglutide effect. (A) Brightfield illumination of NPY-hrGFP neuron from NLT::TRPC5 KO mice. (B) The same neuron under FITC (hrGFP) illumination. (C) Complete dialysis of Alexa Fluor 350 from the intracellular pipette. (D) Merge image illustrates colocalization of hr-GFP and Alexa Fluor 350 indicative of NPY neuron which was deleted of TRPC5. (E) Electrophysiological study demonstrates a TRPC5 deleted NPY-hrGFP neuron that is hyperpolarized in response to liraglutide (1 μM). (F) Histogram summarizing the acute effect of liraglutide (1 μM) on the membrane potential of TRPC5 deleted NPY neurons. (G) Electrophysiological study demonstrates that liraglutide fails to hyperpolarize NPY-hrGFP neuron with the pretreatment of tolbutamide(200 μM). (H) Histogram summarizing the acute effect of liraglutide (1 μM) on the membrane potential of NPY neurons, with the pretreatment of tolbutamide(200 μM). (I) Representative trace showing that liraglutide fails to hyperpolarize NPY-hrGFP neuron from NLT:TrpC5 KO mice with the pretreatment of tolbutamide (200 μM). (J) Histogram summarizing the acute effect of liraglutide (1 μM) on the membrane potential of NPY neurons from NLT:TrpC5 KO mice, with the pretreatment of tolbutamide (200 μM). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM.