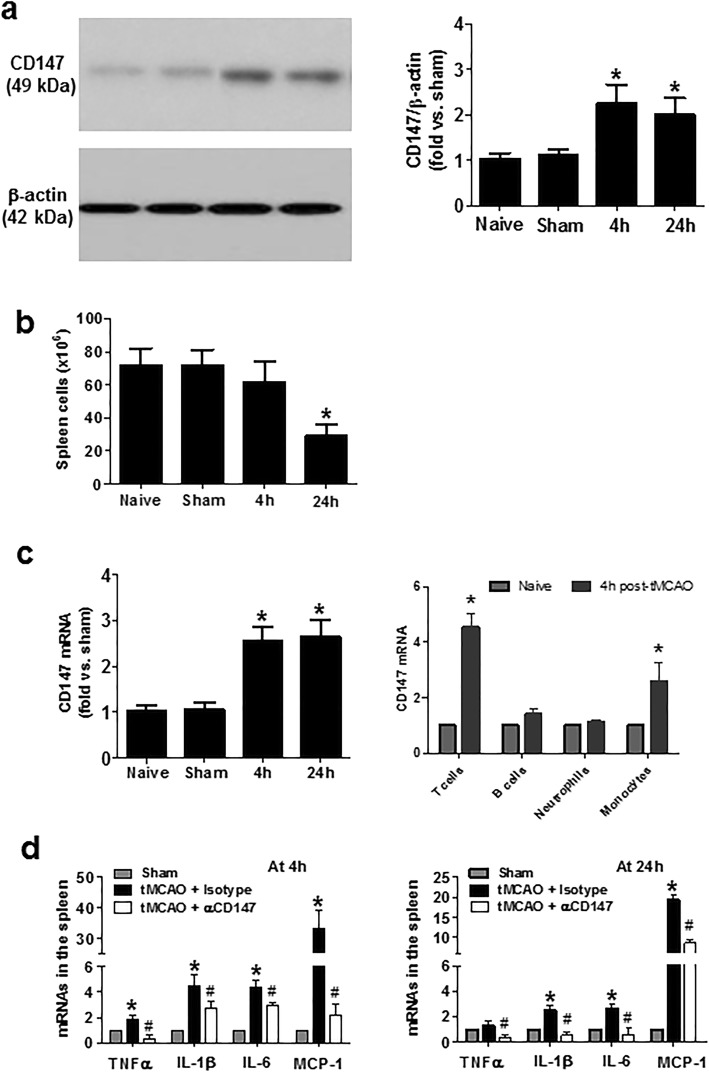
Fig. 1.
Focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion induces CD147 expression and early inflammatory response in the spleen. a Representative western blot images (left) and semi-quantitation (right) showing CD147 protein levels detected in isolated splenocytes from the following groups (n = 5 mice/group): naïve (no surgery), sham surgery, and tMCAO at 4 or 24 h tMCAO. b The number of isolated splenocytes from each of the above indicated groups was counted using a hemocytometer. c RT-qPCR analysis of CD147 mRNA levels detected in isolated whole splenocytes at 4 or 24 h after tMCAO, and in the different subpopulations of splenocytes (T or B cells neutrophils, monocytes) sorted by FACS at 4 h after tMCAO. *p < 0.05 vs. naïve or sham controls. d RT-qPCR analysis of mRNA levels of proinflammatory genes (TNF-α, IL1β, IL6, MCP-1) detected in isolated splenocytes from the following groups (n = 5 me/group): sham surgery, tMCAO + isotype, and tMCAO + αCD147. *p < 0.05 vs. sham; #p < 0.05 vs. tMCAO + isotype