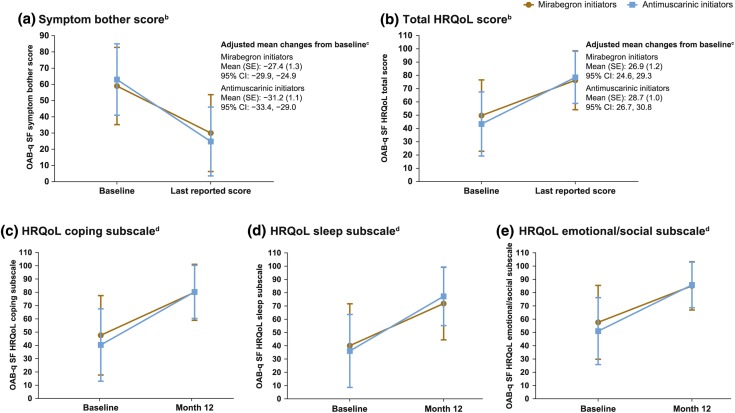
Fig. 2.
Mean (SD) changes in OAB-q SF questionnaire symptom bother score (a), total HRQoL score (b), and coping (c), sleep (d), and emotional/social (e) subscalesa. CI confidence interval, HRQoL health-related quality of life, OAB overactive bladder, OAB-q SF OAB Questionnaire Short-Form, SD standard deviation, SE standard error. aAll scores are transformed scores. If < 50% of the scale items were missing, the scale was retained with the mean scale score of the items present used to impute a score for the missing items. Higher symptom bother scores indicate greater symptom bother. Higher HRQoL subscale and total scores indicate better HRQoL. If ≥ 50% of the items were missing, no scale score was calculated. bBaseline: mirabegron initiators, n = 336; antimuscarinic initiators, n = 602. Last reported score: mirabegron initiators, n = 335; antimuscarinic initiators, n = 603. cGenerated from an analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) model with treatment group, sex, age, and treatment-naïve status as covariates. dChanges in the HRQoL subscales were assessed from baseline to month 12, not last reported score. Baseline: mirabegron initiators, n = 336; antimuscarinic initiators, n = 602. Month 12: mirabegron initiators, n = 310; antimuscarinic initiators, n = 548