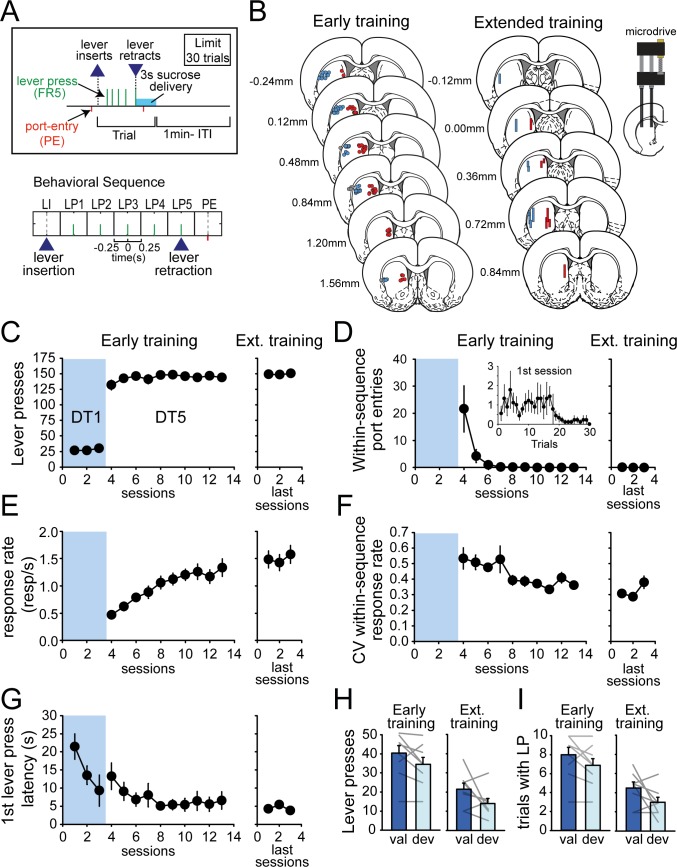
Figure 1. Rats rapidly develop habit and automaticity in the DT5 task.
(A) Schematic of the DT5 task and event-related time intervals considered for analyses. (B) Histological reconstruction of electrode placements in DLS and DMS. (C–G) Number of lever presses (C), within-sequence port entries (D), response rate (responses per second) (E), coefficient of variation of within-sequence response rate (F), and first lever press latency (G) across early training and recording sessions (3 DT1 sessions followed by 10 DT5 sessions) and during the last three recording sessions in the extended training group. Inset in D: Number of within-sequence port entries across trials during the first DT5 session. (H–I) Satiety-induced devaluation: number of lever presses (H) and number of initiated trials (I) in the valued (val) and devalued (deval) conditions under extinction after early training (left) and extended training (right). Error bars show SEM.