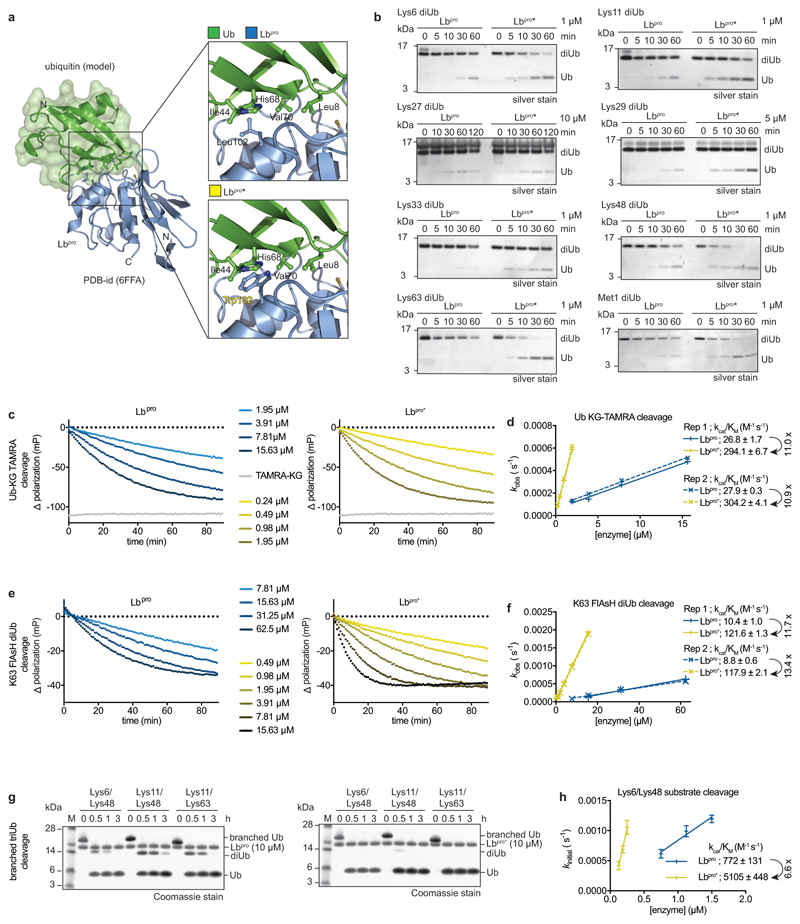
Extended Data Figure 2. Engineered Lbpro has enhanced activity against ubiquitin.
a, Left, structural model of ubiquitin-bound Lbpro as in Extended Data Fig. 1c with ubiquitin under a green surface. Top right, close-up view of the ubiquitin Ile44 patch (Leu8, Ile44, His68, Val70) and its predicted interactions with Lbpro. Differences in the equivalent surface in ISG15 explain its higher affinity 19. Bottom right, modeling of an improved hydrophobic contact between Lbpro and ubiquitin. The corresponding L102W Lbpro mutant is denoted as Lbpro*. b, Diubiquitin cleavage assays, as in Fig. 1a. The cleavage of each diubiquitin (diUb) linkage type was compared for Lbproand Lbpro*. Assays were performed in duplicate. c, Example ubiquitin-KG-TAMRA cleavage assays comparing Lbpro (left) and Lbpro*(right), the difference in polarization relative to a substrate-only negative control is shown. The average trace of assays performed in technical triplicate is shown. TAMRA-KG represents a cleaved product positive control. d, Catalytic efficiencies derived from two independent sets of ubiquitin-KG-TAMRA cleavage measurements as in c. Slope and errors values derived from linear regression are reported for each replicate individually. Fold improvement of Lbpro* over Lbpro in catalytic efficiency towards this substrate is indicated. e, Example diubiquitin K63-FlAsH cleavage assays as in c. f, Catalytic efficiencies derived from two independent sets of diubiquitin K63-FlAsH cleavage measurements as in e. Slope and errors values derived from linear regression are reported for each replicate individually. Fold improvement of Lbpro* over Lbpro in catalytic efficiency towards this substrate is indicated. The REP1 [Lbpro] = 7.81μM data point has been excluded, as reliable exponential decay parameters could not be fitted for this point. g, Branched ubiquitin cleavage assays. Three different branched ubiquitin chains (Lys6/Lys48; Lys11/Lys48; Lys11/Lys63, described in 49) were used in Lbproand Lbpro* cleavage assays. Assays were performed in triplicate. h, Catalytic efficiencies derived from gel-based analysis of three independent Lys6/Lys48 branched triubiquitin cleavage assays performed at three different enzyme concentrations. Fold improvement of Lbpro* over Lbpro in catalytic efficiency towards this substrate is indicated. Centred values correspond to the mean of independent experiments performed in triplicate. Error values represent s.d. from the mean. Slope and errors values derived from linear regression based on the mean values are reported. For gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1.