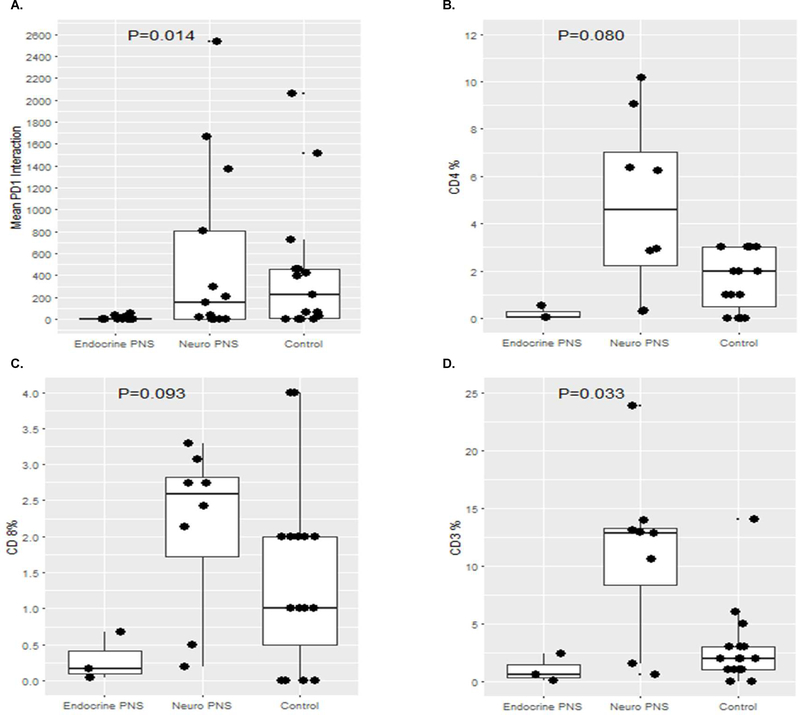
Figure 2. Overall comparison of CD3, CD4, CD8, and PD-1/PD-L1 interaction scores.
Tumors from patients with small cell lung cancer with neurologic paraneoplastic syndromes had significantly increased PD-1/PD-L1 interaction scores (A) compared to tumors from patients with small cell lung cancer with endocrinologic paraneoplastic syndromes and tumors from patients with small cell lung cancer and no paraneoplastic syndrome (“control”). Tumors from patients with small cell lung cancer with neurologic paraneoplastic syndromes had a trend towards increased CD4 (B) and CD8 (C) infiltrates compared to tumors from patients with small cell lung cancer with endocrinologic paraneoplastic syndromes and tumors from patients with small cell lung cancer and no paraneoplastic syndrome (“control”). Tumors from patients with small cell lung cancer with neurologic paraneoplastic syndromes had significantly increased CD3 (D) infiltrates compared to tumors from patients with small cell lung cancer with endocrinologic paraneoplastic syndromes and tumors from patients with small cell lung cancer and no paraneoplastic syndrome (“control”).