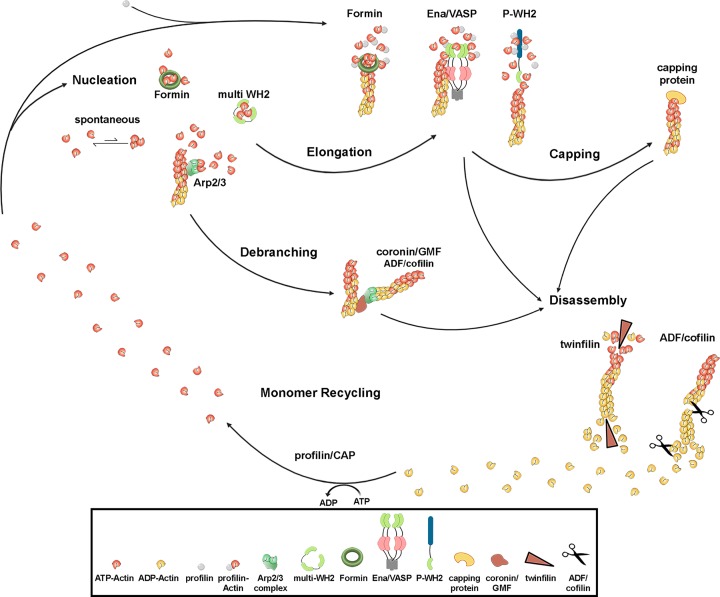
Figure 1. Actin polymerization and turnover.
Diverse factors, such as Arp2/3 complex, various formins or proteins containing multiple actin monomer binding WH2 domains can catalyze nucleation of filaments from ATP-loaded actin monomers. Subsequently, elongation of nascent filaments is achieved by either formins, Ena/VASP proteins or proteins harboring a polyproline-WH2 (P-WH2) module. Elongation can be terminated by capping proteins, for instance heterodimeric capping protein. Filament branches, created by Arp2/3 complex, can be disconnected by proteins of the coronin/GMF as well as cofilin families, whereas twinfilin catalyzes the disassembly of filament ends. Moreover, ADF/cofilin family members are best known for promoting filament disassembly by severing and depolymerization. Recycling of ADP-actin to polymerization-competent ATP-actin is executed by profilin or cyclase-associated protein.