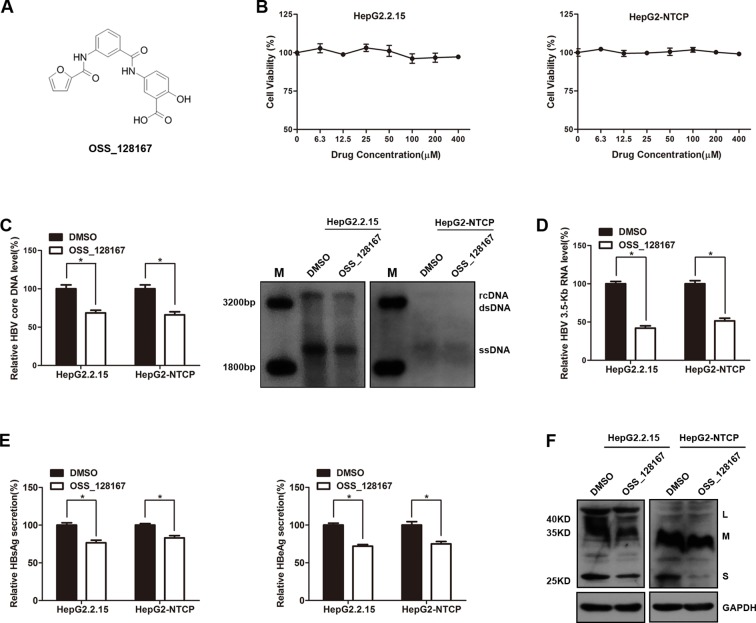
Figure 1.
SIRT6 inhibitor OSS_128167 inhibited hepatitis B virus (HBV) transcription and replication in vitro. (A) Chemical structure of OSS_128167. (B) HepG2.2.15 and HepG2-sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) cells were treated with a series of concentration of OSS_128167. 3 days post-treatment, MTS assay was performed to examine the cytotoxicity of OSS_128167. (C–F) HepG2.2.15 and HBV-infected HepG2-NTCP cells were treated with indicated concentration of OSS_128167. (C) Four days later, cells were harvested to examine HBV core deoxyribonucleic acid level by using real-time PCR and southern blotting analysis. (D) 3.5-Kb ribonucleic acid level was subjected to real-time polymerase chain reaction 3 days after OSS_128167 treatment. (E–F) Secretion of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and hepatitis B envelope antigen were assayed by using ELISA 3 days after treatment. At the same time, HBsAg production in cell lysates was determined by western blotting. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase was used as the loading control. Data represented the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *:P < 0.05.