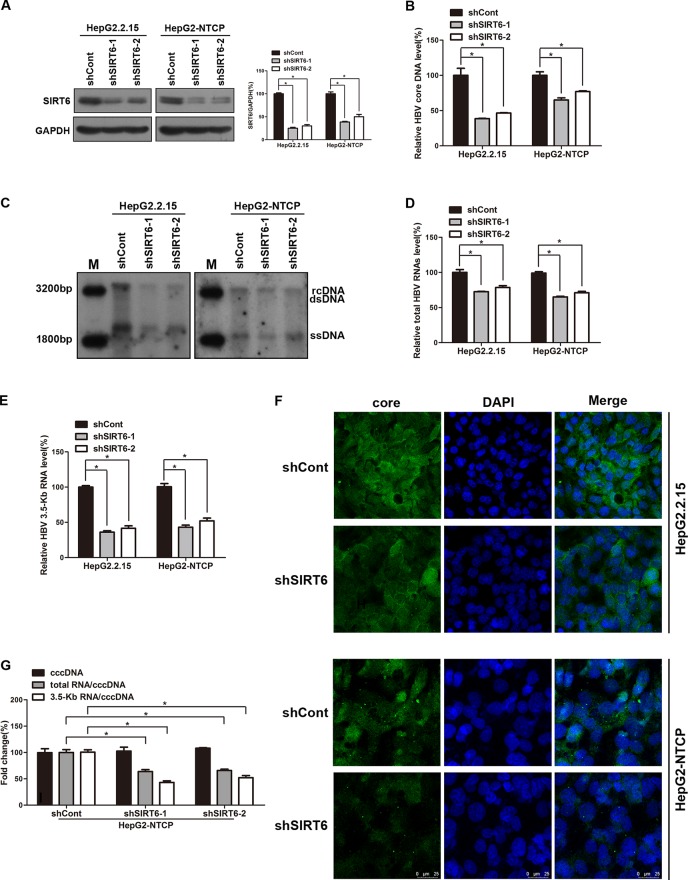
Figure 3.
Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) silencing restricted hepatitis B virus (HBV) transcription and replication. (A–G) HepG2.2.15 and HBV-infected HepG2-sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) cells were transfected with plasmids expressing short hairpin ribonucleic acids (shRNAs) targeting SIRT6 (shSIRT6-1 and shSIRT6-2) or scramble control shRNA (shCont). (A) Total protein was extracted at 4 days post-transfection and subjected to western blotting. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as the loading control. Band intensities were quantified by ImageJ software and normalized to GAPDH. (B, C) HBV core deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) were extracted at 5 days post-transfection. Then real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and southern blotting were performed to detect HBV core DNA level. (D, E) After 4 days post transfection, total RNA was extracted by using TRIzol reagent and total HBV RNAs and 3.5-Kb RNA levels were detected by real-time PCR with specific primers. β-actin was used as the internal control. (F) The core protein was detected by immunofluorescence staining with indicated antibody at 4 days post-transfection and the images were collected by using confocal microscope. (G) HBV-infected HepG2-NTCP cells were transfected with plasmids expressing shRNAs targeting SIRT6 (shSIRT6-1 and shSIRT6-2) or scramble control shRNA (shCont). HBV covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) was extracted and applied for real time PCR. The ratios of total HBV RNAs/cccDNA and 3.5-Kb RNA/cccDNA were calculated. Data represented the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *:P < 0.05.